Page 320 - (DK) The Ultimate Visual Dictionary 2nd Ed.
P. 320
PHYSICS AND CHEMISTR Y
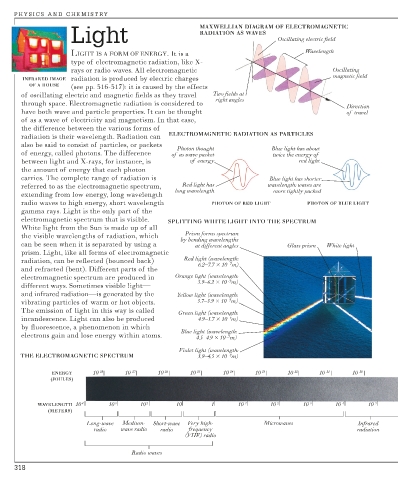
Light MAXWELLIAN DIAGRAM OF ELECTROMAGNETIC
RADIATION AS WAVES
Oscillating electric field
Wavelength
LIGHT IS A FORM OF ENERGY. It is a
type of electromagnetic radiation, like X-
rays or radio waves. All electromagnetic Oscillating
INFRARED IMAGE radiation is produced by electric charges magnetic field
OF A HOUSE (see pp. 316-317): it is caused by the effects
of oscillating electric and magnetic fields as they travel Two fields at
right angles
through space. Electromagnetic radiation is considered to
Direction
have both wave and particle properties. It can be thought of travel
of as a wave of electricity and magnetism. In that case,
the difference between the various forms of
ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION AS PARTICLES
radiation is their wavelength. Radiation can
also be said to consist of particles, or packets
Photon thought Blue light has about
of energy, called photons. The difference of as wave packet twice the energy of
between light and X-rays, for instance, is of energy red light
the amount of energy that each photon
carries. The complete range of radiation is Blue light has shorter
referred to as the electromagnetic spectrum, Red light has wavelength: waves are
long wavelength more tightly packed
extending from low energy, long wavelength
radio waves to high energy, short wavelength PHOTON OF RED LIGHT PHOTON OF BLUE LIGHT
gamma rays. Light is the only part of the
electromagnetic spectrum that is visible. SPLITTING WHITE LIGHT INTO THE SPECTRUM
White light from the Sun is made up of all
Prism forms spectrum
the visible wavelengths of radiation, which
by bending wavelengths
can be seen when it is separated by using a at different angles Glass prism White light
prism. Light, like all forms of electromagnetic
radiation, can be reflected (bounced back) Red light (wavelength:
6.2–7.7 × 10 -7 m)
and refracted (bent). Different parts of the
electromagnetic spectrum are produced in Orange light (wavelength:
5.9–6.2 × 10 -7 m)
different ways. Sometimes visible light—
and infrared radiation—is generated by the Yellow light (wavelength:
vibrating particles of warm or hot objects. 5.7–5.9 × 10 -7 m)
The emission of light in this way is called Green light (wavelength:
incandescence. Light can also be produced 4.9–5.7 × 10 m)
-7
by fluorescence, a phenomenon in which
Blue light (wavelength:
electrons gain and lose energy within atoms. 4.5–4.9 × 10 -7 m)
Violet light (wavelength:
THE ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM 3.9–4.5 × 10 -7 m)
ENERGY 10 -28 10 -27 10 -26 10 -25 10 -24 10 -23 10 -22 10 -21 10 -20
(JOULES)
WAVELENGTH 10 4 10 3 10 2 10 1 10 -1 10 -2 10 -3 10 -4 10 -5
(METERS)
Long-wave Medium- Short-wave Very high- Microwaves Infrared
radio wave radio radio frequency radiation
(VHF) radio
Radio waves
318