Page 319 - (DK) The Ultimate Visual Dictionary 2nd Ed.
P. 319
ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM
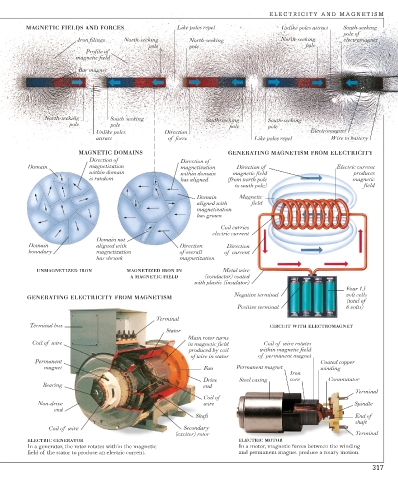
MAGNETIC FIELDS AND FORCES Like poles repel Unlike poles attract South-seeking
pole of
Iron filings North-seeking North-seeking North-seeking electromagnet
pole pole pole
Profile of
magnetic field
Bar magnet
North-seeking South-seeking South-seeking South-seeking
pole pole pole pole
Unlike poles Direction Electromagnet
attract of force Like poles repel Wire to battery
MAGNETIC DOMAINS GENERATING MAGNETISM FROM ELECTRICITY
Direction of Direction of
Domain magnetization magnetization Direction of Electric current
within domain within domain magnetic field produces
is random has aligned (from north pole magnetic
to south pole) field
Domain Magnetic
aligned with field
magnetization
has grown
Coil carries
electric current
Domain not
Domain aligned with Direction Direction
boundary magnetization of overall of current
has shrunk magnetization
UNMAGNETIZED IRON MAGNETIZED IRON IN Metal wire
A MAGNETIC FIELD (conductor) coated
with plastic (insulator)
Four 1.5
Negative terminal volt cells
GENERATING ELECTRICITY FROM MAGNETISM
(total of
Positive terminal 6 volts)
Terminal
Terminal box CIRCUIT WITH ELECTROMAGNET
Stator
Main rotor turns
Coil of wire in magnetic field Coil of wire rotates
produced by coil within magnetic field
of wire in stator of permanent magnet
Permanent Coated copper
magnet Fan Permanent magnet winding
Iron
Drive Steel casing core Commutator
Bearing end
Terminal
Coil of
Non-drive wire Spindle
end
Shaft End of
shaft
Coil of wire Secondary
(exciter) rotor Terminal
ELECTRIC GENERATOR ELECTRIC MOTOR
In a generator, the rotor rotates within the magnetic In a motor, magnetic forces between the winding
field of the stator to produce an electric current. and permanent magnet produce a rotary motion.
317