Page 321 - (DK) The Ultimate Visual Dictionary 2nd Ed.
P. 321
LIGHT
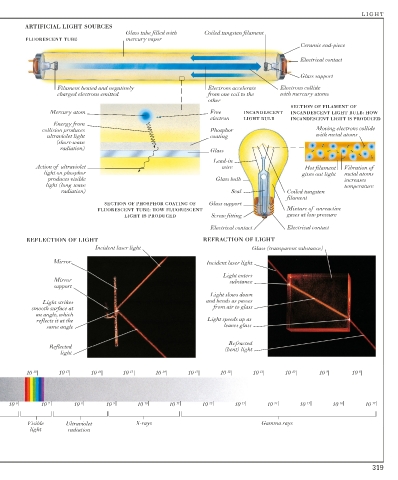
ARTIFICIAL LIGHT SOURCES
Glass tube filled with Coiled tungsten filament
FLUORESCENT TUBE mercury vapor
Ceramic end-piece
Electrical contact
Glass support
Filament heated and negatively Electrons accelerate Electrons collide
charged electrons emitted from one coil to the with mercury atoms
other
SECTION OF FILAMENT OF
Mercury atom Free INCANDESCENT INCANDESCENT LIGHT BULB: HOW
electron LIGHT BULB INCANDESCENT LIGHT IS PRODUCED
Energy from
collision produces Phosphor Moving electrons collide
ultraviolet light coating with metal atoms
(short-wave
radiation)
Glass
Lead-in
Action of ultraviolet wire Hot filament Vibration of
light on phosphor gives out light metal atoms
produces visible Glass bulb increases
light (long-wave temperature
radiation) Seal Coiled tungsten
filament
SECTION OF PHOSPHOR COATING OF Glass support
FLUORESCENT TUBE: HOW FLUORESCENT Mixture of unreactive
LIGHT IS PRODUCED Screw fitting gases at low pressure
Electrical contact Electrical contact
REFLECTION OF LIGHT REFRACTION OF LIGHT
Incident laser light Glass (transparent substance)
Mirror Incident laser light
Light enters
Mirror substance
support
Light slows down
Light strikes and bends as passes
smooth surface at from air to glass
an angle, which
reflects it at the Light speeds up as
same angle leaves glass
Refracted
Reflected (bent) light
light
10 -18 10 -17 10 -16 10 -15 10 -14 10 -13 10 -12 10 -11 10 -10 10 -9 10 -8
10 -6 10 -7 10 -8 10 -9 10 -10 10 -11 10 -12 10 -13 10 -14 10 -15 10 -16 10 -17
Visible Ultraviolet X-rays Gamma rays
light radiation
319