Page 35 - How It Works - Book of Amazing Answers To Curious Questions, 12
P. 35
Science*------------------Q�
How does
diabetes
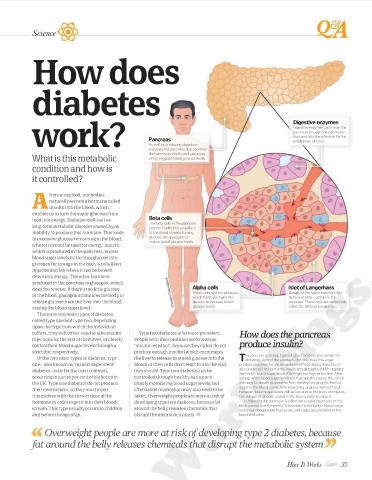
Digestive enzymes
worl<? Pancreas Digestive enzymes pass from the
pancreas through the pancreatic
duct and into the intestine for the
breakdown of food.
As well as producing digestive
enzymes the pancreas also secretes
the hormones insulin and glucagon, ��
What is this metabolic which regulate blood glucose levels.
condition and how is
it controlled?
fter eating food, our bodies
naturally secrete a hormone called
A insulin into the blood, which
enables us to turn the sugar !glucose) from
food into energy. Diabetes mellitus is a Beta cells
The beta cells in the pancreas
long-term metabolic disorder caused by an secrete insulin into a capillary
inability to produce this hormone. This leads to the blood stream, turning
to excessive glucose remaining in the blood, glucose into glycogen to
reduce blood glucose levels.
where it cannot be used for energy. Insulin,
which is produced in the pancreas, lowers
blood sugar levels by turning glucose into
glycogen for storage in the body's cells !liver,
muscles and fat) where it can be broken
down into energy. The other hormone
produced in the pancreas is glucagon, which
does the reverse. If there's too little glucose Alpha cells Islet of Langerhans
These cells secrete glucagon, Groups of hormone-making cells
in the blood, glucagon stimulates the body to which turns glycogen into alpha and beta - gather in the
release glucose from the liver into the blood, glucose to increase blood pancreas. These cells are collectively
raising the blood sugar level. glucose levels. called the Islets of Langerhans.
There are two main types of diabetes,
called type one and type two. Depending
upon the type from which the individual
suffers, they will either need to take insulin Type two diabetes is far more prevalent. How does the pancreas
injections for the rest of their lives, or closely People with this condition are known as produce insu
control their blood sugar levels through a 'insulin resistant', because they either do not
strict diet respectively. produce enough insulin !which encourages
The pancreas is a long, tapered gland located deep inside the
Of the two main types of diabetes, type the liver to release its stored glucose into the I abdomen, behind the stomach. Not only does this organ
one- also known as 'insulin dependent' blood) or their cells don't react to it in the way produce enzymes for the breakdown of food during digestion, it
diabetes- is by far the least common, they should. Type two diabetes can be also produces the hormones insulin and glucagon, which regulate
the body's blood sugar levels if they get too high or too low. After
occurring in just 10 per cent of diabetics in controlled through healthy eating and eating, when blood sugar levels are high, insulin causes the cells in
the UK. Type one diabetics do not produce closely monitoring blood sugar levels, but the body to absorb glucose for fuel, thereby bringing the level of
sugar in the blood down. After exercising or going without food,
their own insulin, so they must inject often tablet medication may also need to be
however, blood sugar levels will be low and so the body stimulates
themselves with the correct dose of the taken. Overweight people are more at risk of the release of glucose stored in the liver in order to raise it.
hormone in order to get it into their blood developing type two diabetes, because fat In diabetics the pancreas is either not producing insulin, or the
body cannot use it properly. Subsequently the body's blood sugar
stream. This type usually occurs in children around the belly releases chemicals that levels rise dangerously high as unused sugar accumulates in the
and before the age of 40. disrupt the metabolic system. blood and urine.
Overweight people are more at risk of developing type 2 diabetes, because
fat around the belly releases chemicals that disrupt the metabolic system
WorldMags.net
WorldMags.net How It T%rks 35