Page 36 - How It Works - Book of Amazing Answers To Curious Questions, 12
P. 36
AMAZIG ANSWERS TO CURIOUS QUESTIONS
What's inside cerebellum co-ordinates
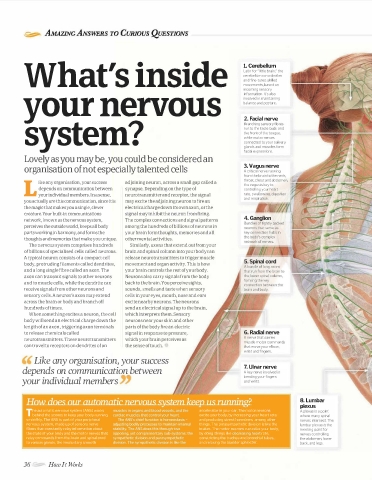
1. Cerebellum
Latin for "little brain," the
and fine·tunes skilled
movements, based on
incoming sensory
your nervous balance and posture.
information. It's also
involved in maintaining
2. Facial nerve
system? run to the taste buds and
Branching sensory fibres
the front of the tongue,
while motor nerves
connected to your salivary
glands and muscles form
facial expressions.
Lovely as you may be, you could be considered an
organisation of not especially talented cells 3. Vagus nerve
A critical nerve running
from the brain to the neck,
throat, chest and abdomen,
ike any organisation, your success adjoining neuron, across a small gap called a
the vagus is key to
depends on communication between synapse. Depending on the type of controlling your heart
L your individual members. lna sense, neurotransmitter and receptor, the signal rate, swallowing, digestion
and respiration.
you actually are this communication, since it is may excite the adjoining neuron to fire an
the magic that makes you a single, clever electrical charge down its own axon, or the
creature. Your built-in communications signal may inhibit the neuron from firing.
network, known as the nervous system, The complex connections and signal patterns
perceives the outside world, keeps all body among the hundreds of billions of neurons in
parts working in harmony, and forms the your brain form thoughts, memories and all
thoughts and memories that make you unique. other mental activities.
The nervous system comprises hundreds Similarly, axons that extend out from your
of billions of specialised cells called neurons. brain and spinal column into yourbodycan
A typical neuron consists of a compact cell release neurotransmitters to trigger muscle
body, protruding filaments called dendrites, movement and organ activity. This is how
and a long single fibre called an axon. The your brain controls the rest ofyourbody.
axon can transmit signals to other neurons Neurons also carry signals from the body
and to muscle cells, while the dendrite can back to the brain. You perceive sights,
receive signals from other neurons and sounds, smells and taste when sensory
sensory cells. A neuron's axon may extend cells in your eyes, mouth, nose and ears
across the brain or body and branch off excite nearby neurons. The neurons
hundreds of times. send an electrical signal up to the brain,
When something excites a neuron, the cell which interprets them. Sensory
body will send an electrical charge down the neurons near your skin and other
length of an axon, triggering axon terminals parts of the body fire an electric
to release chemicals called signal in response to pressure,
neurotransmitters. These neurotransmitters which your brain perceives as A nerve that carries
muscle motor commands
can travel to receptors on dendrites of an the sense of touch. that move your elbow,
wrist and fingers.
Like any organisation, your success
depends on communication between 7. Ulnar nerve
A key nerve involved in
your individual members bending your fingers
and wrist.
B. lumbar
plexus
ilille autornatrr: nervous system (ANS) works accelerator rn your car The motor rwtuons A plexus is a point
behrnd the SCtlnes to keep your body runnrng excrte your body, by rncr eas111q your he.1r t rate where many spinal
smoothly The ANS ts rar t of yow pPnpiJ ral and pr oducmg 5tt esc: l•or manes, among othet nerves intersect. The
nervous system made up of scns01 y nerve thrngs. The pJrasympathcltc dtvrSion •s hkc the lumbar plexus is the
frbres tllill const;mtly relay rnfouniltton about br<1hes. The motor nr.ttrons can r Pltlx yOUI body, meeting point for
the state of your body and the motor nerves thJt bv dornq tl11ngs lrke clt?creasrnc l ltear t rate nerves controlling
rPiay romrnanris from the brarn .Jnrl spural cord consrrrclu1g the trachea Jnd hr onchral tul:ies the abdomen, lower
to vcmotrs gl"mds, the uwoltmtar y smooth amt relaxrng the bladder spluncwr back, and legs.
36 How It TtOrks WorldMags.net
WorldMags.net