Page 40 - How It Works - Book of Amazing Answers To Curious Questions, 12
P. 40
AMAZIG ANSWERS TO CURIOUS QUESTIONS -------------------
What's in our ears?
The ear performs a range of functions,
sending messages to the brain when
a sound is made while also providing
your body with a sense of balance
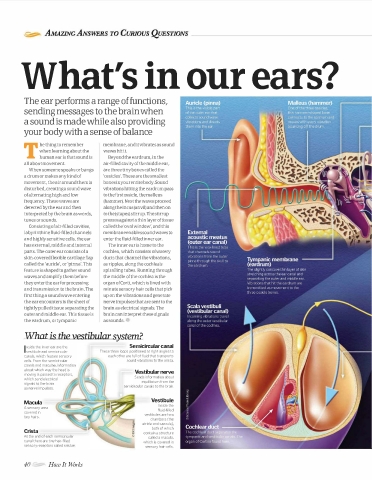
he thing to remember membrane, and it vibrates as sound
when learning about the waves hit it.
T human ear is that sound is Beyond the eardrum, in the
all about movement. air-filled cavity of the middle ear,
When someone speaks or bangs are three tiny bones called the
a drum or makes any kind of 'ossicles'. These are the smallest
movement, the air around them is bones in your entire body. Sound
disturbed, creating a sound wave vibrations hitting the eardrum pass
of alternating high and low to the first ossicle, the malleus
frequency. These waves are (hammer). Next the waves proceed
detected by the ear and then along the incus (anvil) and then on
interpreted by the brain as words, to the (stapes) stirrup. The stirrup
tunes or sounds. presses against a thin layer of tissue
Consisting of air-filled cavities, called the 'oval window', and this
labyrinthine fluid-filled channels membrane enables sound waves to
and highly sensitive cells, the ear enter the fluid-filled inner ear.
has external, middle and internal The inner ear is home to the
parts. The outerearconsists of a cochlea, which consists of watery
skin-covered flexible cartilage flap ducts that channel the vibrations,
called the 'auricle', or 'pinna'. This as ripples, along the cochlea's
feature is shaped to gather sound spiralling tubes. Running through
waves and amplify them before the middle of the cochlea is the
they enter the ear for processing organ of Corti, which is lined with
and transmission to the brain. The minute sensory hair cells that pick
first thing a sound wave entering up on the vibrations and generate
the ear encounters is the sheet of nerve impulses that are sent to the
tightly pulled tissue separating the brain as electrical signals. The
outer and middle ear. This tissue is brain can interpret these signals
the eardrum, or tympanic as sounds.
What is the vestar syst?
nside the inner ear are the Semicircular canal
Ivestibule and semicircular These three loops positioned at right angles to
canals, which feature sensory each other are full of fluid that transports
cells. From the semicircular sound vibrations to the crista.
canals and maculae, information
about which way the head is
moving is passed to receptors, Vestibular nerve
which send electrical Sends information about
signals to the brain equilibrium from the
as nerve impulses. semicircular canals to the brain.
Vestibule
Macula
Inside the
A sensory area fluid·filled
covered in vestibules are two
tiny hairs.
chambers (the
utricle and saccule),
both of which
Crista contain a structure
At the end of each semicircular called a macula,
canal there are tiny hair-filled which is covered in
sensory receptors called cristae. sensory hair cells.
40 How It TtOrks WorldMags.net
WorldMags.net