Page 39 - How It Works - Book of Amazing Answers To Curious Questions, 12
P. 39
Science*------------------Q�
What mal<es paint dry?
Pivotal to its application, the drying mechanism of
paint tells us much about its formulation
he majority of paints dry through transmitted light, giving paint its colourisation. evaporation of a solvent-with cure adhesion
evaporation, a process that allows its They can be ascertained either naturally or attained bypolymerisation (molecules bonding
T pigmentation to be set onto a chosen produced synthetically. together in a chemical reaction). Binders are
surface purely by being exposed to the The pigments of paint are given their paint arguably the key component of paint, as without
surrounding atmosphere. However, the drying structure by binders, synthetic or natural resins them it would never stick to a surface long
process can vary and is often complicated and such as acrylics, polyesters or oils that impart enough to dry.
altered between different paint types. adhesion and influence durability and Finally, paint additives help to conjoin the
Paints usually contain three key components: flexibility. Crucially, though, binders can also other components and aid application, structure
pigments, binders and additives. Pigments are play a role in how paint dries, curing it as well as and drying. Certain additives are often used as
dry, insoluble powders that by wavelength supplying it with adhesion. It is important to catalysts for polymerisation, while others are
selective absorption (ie they only reflect certain note that curing is a different process to drying included to prevent the clumping of paint orin
wavelengths) change the colour of reflected or -which, as mentioned before, is caused by order to alter its viscosity.
-------------------------------------------- �� --------------------------------------------
How do blood transfusions worl<?
Whether it's a patient haemorrhaging to death or a 'top up' for
life-long diseases, blood transfusions are vital procedures
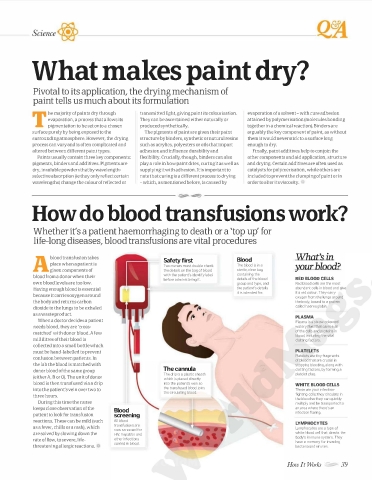
blood transfusion takes Safety first Blood What's in
place when a patient is Two nurses must double check The blood is in a your blood?
A given components of the details on the bag of blood sterile, clear bag
blood from a donor when their with the patient's identify label containing the
before administering it. details of the blood RED BLOOD CELLS
own blood levels are too low. group and type, and Red blood cells are the most
Having enough blood is essential the patient's details abundant cells in blood and give
it is intended for. it a red colour. They carry
because it carries oxygen around oxygen from the lungs around
the body and returns carbon the body, bound to a protein
dioxide to the lungs to be exhaled called haemoglobin.
as a waste product.
PLASMA
When a doctor decides a patient Plasma is a straw-coloured
needs blood, they are 'cross watery fluid that carries all
matched' with donor blood. A few of the cells and proteins in
blood, including the vital
millilitres of their blood is clotting factors.
collected into a small bottle which
must be hand-labelled to prevent PLATELETS
Platelets are tiny fragments
confusion between patients. In
of blood that are crucial in
the lab the blood is matched with stopping bleeding, along with
donor blood of the same group The cannula clotting factors, by forming a
The drip is a plastic sheath platelet plug.
(either A, B or 0). The unit of donor
which is placed directly
blood is then transfused via a drip into the patient's vein so WHITE BLOOD CELLS
the transfused blood joins
into the patient's vein over two to These are your infection
the circulating blood.
three hours. fighting cells; they circulate in
the blood so they can quickly
During this time the nurse multiply and be transported to
keeps close observation of the Blood an area where there's an
patient to look for transfusion screening infection flaring.
reactions. These can be mild (such All blood LYMPHOCYTES
transfusions are
as a fever, chills or a rash), which Lymphocytes are a type of
now screened for
are solved by slowing down the HIV, hepatitis and white blood cell that directs the
body's immune system. They
rate of flow, to severe, life other infections
carried in blood. have a memory for invading
threatening allergic reactions. bacteria and viruses.
WorldMags.net How It T%rks 39
WorldMags.net