Page 209 - (DK) Ocean - The Definitive Visual Guide
P. 209
CLASSIFICATION 207
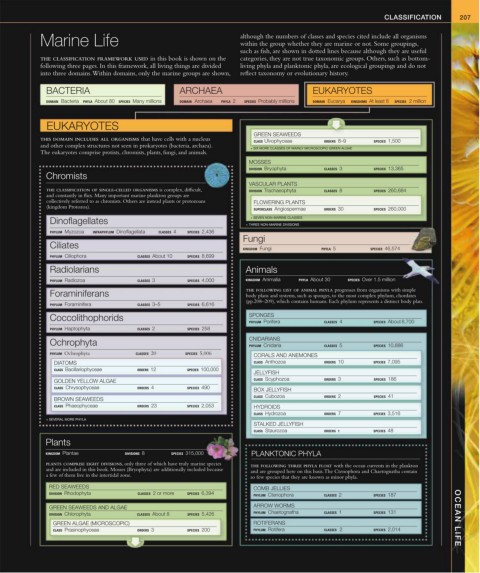
Marine Life although the numbers of classes and species cited include all organisms
within the group whether they are marine or not. Some groupings,
such as fish, are shown in dotted lines because although they are useful
THE CLASSIFICATION FRAMEWORK USED in this book is shown on the categories, they are not true taxonomic groups. Others, such as bottom-
following three pages. In this framework, all living things are divided living phyla and planktonic phyla, are ecological groupings and do not
into three domains. Within domains, only the marine groups are shown, reflect taxonomy or evolutionary history.
BACTERIA ARCHAEA EUKARYOTES
DOMAIN Bacteria PHYLA About 80 SPECIES Many millions DOMAIN Archaea PHYLA 2 SPECIES Probably millions DOMAIN Eucarya KINGDOMS At least 8 SPECIES 2 million
EUKARYOTES
GREEN SEAWEEDS
THIS DOMAIN INCLUDES ALL ORGANISMS that have cells with a nucleus CLASS Ulvophyceae ORDERS 8–9 SPECIES 1,500
and other complex structures not seen in prokaryotes (bacteria, archaea).
+ SIX MORE CLASSES OF MAINLY MICROSCOPIC GREEN ALGAE
The eukaryotes comprise protists, chromists, plants, fungi, and animals.
MOSSES
DIVISION Bryophyta CLASSES 3 SPECIES 13,365
Chromists
VASCULAR PLANTS
THE CLASSIFICATION OF SINGLE-CELLED ORGANISMS is complex, difficult, DIVISION Trachaeophyta CLASSES 8 SPECIES 260,684
and constantly in flux. Many important marine plankton groups are
collectively referred to as chromists. Others are instead plants or protozoans FLOWERING PLANTS
(kingdom Protozoa).
SUPERCLASS Angiospermae ORDERS 30 SPECIES 260,000
Dinoflagellates + SEVEN NON-MARINE CLASSES
+ THREE NON-MARINE DIVISIONS
PHYLUM Myzozoa INFRAPHYLUM Dinoflagellata CLASSES 4 SPECIES 2,436
Fungi
Ciliates KINGDOM Fungi PHYLA 5 SPECIES 46,574
PHYLUM Ciliophora CLASSES About 10 SPECIES 8,699
Radiolarians Animals
PHYLUM Radiozoa CLASSES 3 SPECIES 4,000 KINGDOM Animalia PHYLA About 30 SPECIES Over 1.5 million
Foraminiferans THE FOLLOWING LIST OF ANIMAL PHYLA progresses from organisms with simple
body plans and systems, such as sponges, to the most complex phylum, chordates
PHYLUM Foraminifera CLASSES 3–5 SPECIES 6,616 (pp.208–209), which contains humans. Each phylum represents a distinct body plan.
Coccolithophorids SPONGES
PHYLUM Porifera CLASSES 4 SPECIES About 8,700
PHYLUM Haptophyta CLASSES 2 SPECIES 258
Ochrophyta CNIDARIANS CLASSES 5 SPECIES 10,886
PHYLUM Cnidaria
PHYLUM Ochrophyta CLASSES 20 SPECIES 5,006 CORALS AND ANEMONES
DIATOMS CLASS Anthozoa ORDERS 10 SPECIES 7,095
CLASS Bacillariophyceae ORDERS 12 SPECIES 100,000
JELLYFISH
GOLDEN YELLOW ALGAE CLASS Scyphozoa ORDERS 3 SPECIES 186
CLASS Chrysophyceae ORDERS 4 SPECIES 490 BOX JELLYFISH
BROWN SEAWEEDS CLASS Cubozoa ORDERS 2 SPECIES 41
CLASS Phaeophyceae ORDERS 23 SPECIES 2,053 HYDROIDS
CLASS Hydrozoa ORDERS 7 SPECIES 3,516
+ SEVERAL MORE PHYLA
STALKED JELLYFISH
CLASS Staurozoa ORDERS 1 SPECIES 48
Plants
KINGDOM Plantae DIVISIONS 8 SPECIES 315,000 PLANKTONIC PHYLA
PLANTS COMPRISE EIGHT DIVISIONS, only three of which have truly marine species THE FOLLOWING THREE PHYLA FLOAT with the ocean currents in the plankton
and are included in this book. Mosses (Bryophyta) are additionally included because and are grouped here on this basis. The Ctenophora and Chaetognatha contain
a few of them live in the intertidal zone.
so few species that they are known as minor phyla.
RED SEAWEEDS COMB JELLIES
DIVISION Rhodophyta CLASSES 2 or more SPECIES 6,394 PHYLUM Ctenophora CLASSES 2 SPECIES 187
GREEN SEAWEEDS AND ALGAE ARROW WORMS
DIVISION Chlorophyta CLASSES About 8 SPECIES 5,426 PHYLUM Chaetognatha CLASSES 1 SPECIES 131 OCEAN LIFE
GREEN ALGAE (MICROSCOPIC) ROTIFERANS
CLASS Prasinophyceae ORDERS 3 SPECIES 200 PHYLUM Rotifera CLASSES 2 SPECIES 2,014