Page 49 - Fish and Amphibians (Britannica Illustrated Science Library)
P. 49
44 DIVERSITY FISH AND AMPHIBIANS 45
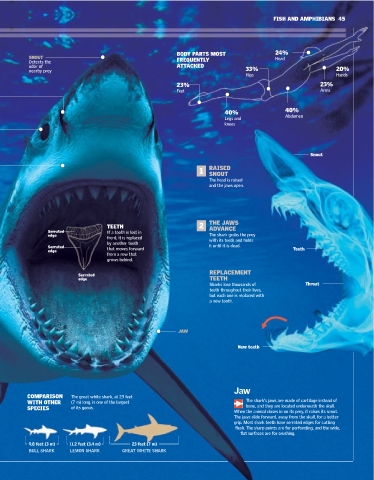
Deadly Weapon SNOUT BODY PARTS MOST 24%
Head
FREQUENTLY
Detects the
odor of ATTACKED
nearby prey 33% 20%
ne of the greatest predators in the ocean is the great white shark, Hips Hands
easily identified by its distinctive white coloring, black eyes, and fierce 23% 23%
O teeth and jaws. Many biologists believe that attacks on humans result Feet Arms
from the shark's exploratory behavior, because these fish often lift their NASAL
PITS
heads above the water and explore things by biting them. This activity is 40%
40%
often dangerous because of the sharpness of the sharks' teeth and the Abdomen
Legs and
strength of their jaws. Great white sharks are implicated in most fatal shark knees
attacks on humans, especially on surfers and divers. EYES
They have
poor vision
and use their
sense of
Senses SHARK ATTACKS 23 smell to hunt. Snout
MEDITERRANEAN
1876-2004
Sharks have senses that most JAW RAISED
animals lack. The ampullae of During an 1
attack, it SNOUT
Lorenzini are small clefts in the shark's
stretches
head that detect electricity. This sense forward. The head is raised
helps them find prey hidden in the sand. and the jaws open.
The lateral line is used to detect movement 84 8 2
or sound underwater. Smell is their most WEST EAST JAPAN
COAST COAST 1
advanced sense, and it occupies two thirds OF U.S. OF U.S.
of their brain. They also have a highly SOUTH
KOREA
developed sense of hearing, which allows 1
them to detect very low-frequency sounds. MEXICO THE JAWS
3 TEETH 2 ADVANCE
SOUTH 10 Serrated If a tooth is lost in The shark grabs the prey
AMERICA NEW edge front, it is replaced with its teeth and holds
47 41 ZEALAND by another tooth it until it is dead.
Hearing Ampulla of SOUTH AFRICA AUSTRALIA Serrated that moves forward Teeth
Detects sounds Lorenzini edge from a row that
of very low Detects nerve
frequency impulses grows behind.
220 Serrated REPLACEMENT Throat
TEETH
edge
Sharks lose thousands of
FIN
ATTACKS IN DORSAL teeth throughout their lives,
but each one is replaced with
128 YEARS a new tooth.
Nose
The most highly
Lateral line developed sense JAW
detects is smell; it takes
movements or up two thirds of
sounds the brain.
underwater. New teeth
Electric ANAL
radar
CAUDAL FIN FIN
The great white
shark has a large
heterocercal
caudal fin.
Jaw
GREAT WHITE COMPARISON The great white shark, at 23 feet
SHARK WITH OTHER (7 m) long, is one of the largest The shark's jaws are made of cartilage instead of
Carcharodon SPECIES of its genus. bone, and they are located underneath the skull.
carcharias When the animal closes in on its prey, it raises its snout.
The jaws slide forward, away from the skull, for a better
PECTORAL FIN PELVIC FIN grip. Most shark teeth have serrated edges for cutting
Habitat Oceans Highly developed flesh. The sharp points are for perforating, and the wide,
and very important
Weight 4,400 pounds (2,000 kg) flat surfaces are for crushing.
for swimming
Length 23 feet (7 m)
9.8 feet (3 m) 11.2 feet (3.4 m) 23 feet (7 m)
Life span 30-40 years
BULL SHARK LEMON SHARK GREAT WHITE SHARK