Page 4 - Nilam_Publication_module_Chemistry_Form.pdf
P. 4
MODULE • Chemistry Form 4
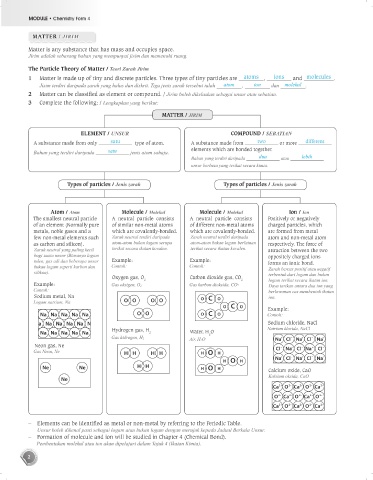
MATTER / JIRIM
Matter is any substance that has mass and occupies space.
Jirim adalah sebarang bahan yang mempunyai jisim dan memenuhi ruang.
The Particle Theory of Matter / Teori Zarah Jirim
1 Matter is made up of tiny and discrete particles. Three types of tiny particles are atoms , ions and molecules .
Jisim terdiri daripada zarah yang halus dan diskrit. Tiga jenis zarah tersebut ialah atom , ion dan molekul .
2 Matter can be classified as element or compound. / Jirim boleh dikelaskan sebagai unsur atau sebatian.
3 Complete the following: / Lengkapkan yang berikut:
MATTER / JIRIM
ELEMENT / UNSUR COMPOUND / SEBATIAN
A substance made from only satu type of atom. A substance made from two or more different
Bahan yang terdiri daripada satu jenis atom sahaja. elements which are bonded together.
Bahan yang terdiri daripada dua atau lebih
unsur berbeza yang terikat secara kimia.
Types of particles / Jenis zarah Types of particles / Jenis zarah
Atom / Atom Molecule / Molekul Molecule / Molekul Ion / Ion
The smallest neutral particle A neutral particle consists A neutral particle consists Positively or negatively
of an element (Normally pure of similar non-metal atoms of different non-metal atoms charged particles, which
metals, noble gases and a which are covalently-bonded. which are covalently-bonded. are formed from metal
few non-metal elements such Zarah neutral terdiri daripada Zarah neutral terdiri daripada atom and non-metal atom
as carbon and silicon). atom-atom bukan logam serupa atom-atom bukan logam berlainan respectively. The force of
Zarah neutral yang paling kecil terikat secara ikatan kovalen. terikat secara ikatan kovalen. attraction between the two
bagi suatu unsur (Biasanya logam oppositely charged ions
tulen, gas adi dan beberapa unsur Example: Example: forms an ionic bond.
bukan logam seperti karbon dan Contoh: Contoh: Zarah bercas positif atau negatif
silikon). terbentuk dari logam dan bukan
Oxygen gas, O 2 Carbon dioxide gas, CO 2
Example: Gas oksigen, O2 Gas karbon dioksida, CO2 logam terikat secara ikatan ion.
Daya tarikan antara dua ion yang
Contoh: berlawanan cas membentuk ikatan
Sodium metal, Na O C O ion.
Logam natrium, Na O O O O
O C O Example:
Na Na Na Na Na O O O C O Contoh:
Na Na Na Na Na Na Sodium chloride, NaCl
Hydrogen gas, H Natrium klorida, NaCl
Na Na Na Na Na 2 Water, H O
2
Gas hidrogen, H2 Air, H2O Na Cl – Na Cl – Na +
+
+
Neon gas, Ne Cl – Na Cl – Na + Cl –
+
Gas Neon, Ne H H H H H O H
+
+
H O H Na Cl – Na Cl – Na +
Ne Ne H H H O H Calcium oxide, CaO
Ne Kalsium oksida, CaO
Ca 2+ O 2– Ca 2+ O 2– Ca 2+
O 2– Ca 2+ O 2– Ca 2+ O 2–
Ca 2+ O 2– Ca 2+ O 2– Ca 2+
– Elements can be identified as metal or non-metal by referring to the Periodic Table.
Unsur boleh dikenal pasti sebagai logam atau bukan logam dengan merujuk kepada Jadual Berkala Unsur.
– Formation of molecule and ion will be studied in Chapter 4 (Chemical Bond).
Pembentukan molekul atau ion akan dipelajari dalam Tajuk 4 (Ikatan Kimia).
2
Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
01-Chem F4 (3p).indd 2 12/9/2011 5:59:27 PM