Page 68 - Nilam_Publication_module_Chemistry_Form.pdf
P. 68
MODULE • Chemistry Form 4
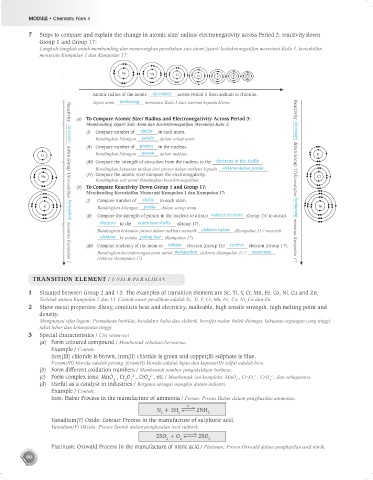
7 Steps to compare and explain the change in atomic size/ radius/ electronegativity across Period 3, reactivity down
Group 1 and Group 17:
Langkah-langkah untuk membanding dan menerangkan perubahan saiz atom/ jejari/ keelekronegatifan merentasi Kala 3, kereaktifan
menuruni Kumpulan 1 dan Kumpulan 17:
16 p
Atomic radius of the atoms decreases across Period 3 from sodium to chlorine.
Jejari atom berkurang merentasi Kala 3 dari natrium kepada klorin.
(a) To Compare Atomic Size/ Radius and Electronegativity Across Period 3:
Membanding Jejari/ Saiz Atom dan Keelektronegatifan Merentasi Kala 3:
Reactivity
(i) Compare number of shells in each atom.
Bandingkan bilangan petala dalam setiap atom.
increases
(ii) Compare number of proton in the nucleus.
Bandingkan bilangan proton dalam nukleus.
Li F
(iii) Compare the strength of attraction from the nucleus to the electrons in the shells .
Bandingkan kekuatan tarikan dari proton dalam nukleus kepada elektron dalam petala .
(iv) Compare the atomic size/ Compare the electronegativity.
Na Cl
Bandingkan saiz atom/ Bandingkan keelektronegatifan. Reactivity decreases down Group 17/Kereaktifan berkurang menurun Kumpulan 17
(b) To Compare Reactivity Down Group 1 and Group 17:
Membanding Kereaktifan Menuruni Kumpulan 1 dan Kumpulan 17:
(i) Compare number of shells in each atom.
K down Group 1/Kereaktifan bertambah menurun Kumpulan 1 Bandingkan bilangan petala dalam setiap atom. Br
(ii) Compare the strength of proton in the nucleus to attract valence electron (Group 1)// to attract
electron to the outermost shells (Group 17).
Bandingkan kekuatan proton dalam nukleus menarik elektron valens (Kumpulan 1) // menarik
elektron ke petala paling luar (Kumpulan 17).
(iii) Compare tendency of the atom to release electron (Group 1)// receive electron (Group 17).
Bandingkan kecenderungan atom untuk melepaskan elektron (Kumpulan 1) // menerima
elektron (Kumpulan 17).
TRANSITION ELEMENT / UNSUR PERALIHAN
1 Situated between Group 2 and 13. The examples of transition element are Sc, Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu and Zn.
Terletak antara Kumpulan 2 dan 13. Contoh unsur peralihan adalah Sc, Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu dan Zn.
2 Show metal properties: Shiny, conducts heat and electricity, malleable, high tensile strength, high melting point and
density.
Mempunyai sifat logam: Permukaan berkilat, konduktor haba dan elektrik, bersifat mulur, boleh ditempa, kekuatan tegangan yang tinggi,
takat lebur dan ketumpatan tinggi.
3 Special characteristics / Ciri istimewa:
(a) Form coloured compound / Membentuk sebatian berwarna.
Example / Contoh:
Iron(III) chloride is brown, iron(II) chloride is green and copper(II) sulphate is blue.
Ferum(III) klorida adalah perang, ferum(II) klorida adalah hijau dan kuprum(II) sulfat adalah biru.
(b) Form different oxidation numbers / Membentuk nombor pengoksidaan berbeza.
(c) Form complex ions: MnO , Cr O , CrO , etc / Membentuk ion kompleks: MnO , Cr O , CrO , dan sebagainya.
2–
–
2–
–
2–
2–
4
2
4
4
7
4
2
7
(d) Useful as a catalyst in industries / Berguna sebagai mangkin dalam industri.
Example / Contoh:
Iron: Haber Process in the manufacture of ammonia / Ferum: Proses Haber dalam penghasilan ammonia.
Fe
N + 3H 2NH
2 2 3
Vanadium(V) Oxide: Contact Process in the manufacture of sulphuric acid.
Vanadium(V) Oksida: Proses Sentuh dalam penghasilan asid sulfurik.
2SO + O 2SO
2 2 3
Platinum: Ostwald Process in the manufacture of nitric acid / Platinum: Proses Ostwald dalam penghasilan asid nitrik.
66
Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
03-Chem F4 (3P).indd 66 12/9/2011 5:57:56 PM