Page 37 - Applied Statistics with R
P. 37
3.2. DATA STRUCTURES 37
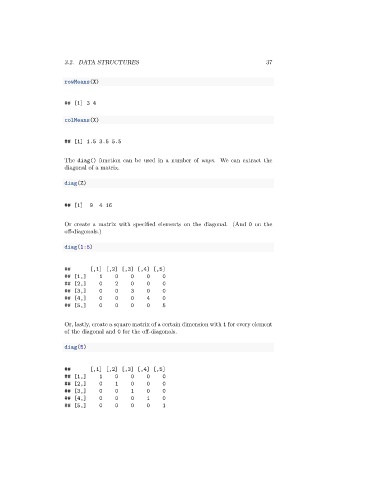
rowMeans(X)
## [1] 3 4
colMeans(X)
## [1] 1.5 3.5 5.5
The diag() function can be used in a number of ways. We can extract the
diagonal of a matrix.
diag(Z)
## [1] 9 4 16
Or create a matrix with specified elements on the diagonal. (And 0 on the
off-diagonals.)
diag(1:5)
## [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5]
## [1,] 1 0 0 0 0
## [2,] 0 2 0 0 0
## [3,] 0 0 3 0 0
## [4,] 0 0 0 4 0
## [5,] 0 0 0 0 5
Or, lastly, create a square matrix of a certain dimension with 1 for every element
of the diagonal and 0 for the off-diagonals.
diag(5)
## [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5]
## [1,] 1 0 0 0 0
## [2,] 0 1 0 0 0
## [3,] 0 0 1 0 0
## [4,] 0 0 0 1 0
## [5,] 0 0 0 0 1