Page 234 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 234
190 SEcTioN ii Microbiology ` microbiology—aNtimicrobials Microbiology ` microbiology—aNtimicrobials
Carbapenems Doripenem, Imipenem, Meropenem, Ertapenem (DIME antibiotics are given when there is a
10/10 [life-threatening] infection).
mecHaNism Imipenem is a broad-spectrum, β-lactamase– With imipenem, “the kill is lastin’ with
resistant carbapenem. Always administered cilastatin.”
with cilastatin (inhibitor of renal Newer carbapenems include ertapenem (limited
dehydropeptidase I) to inactivation of drug Pseudomonas coverage) and doripenem.
in renal tubules.
cliNical Use Gram ⊕ cocci, gram ⊝ rods, and anaerobes.
Wide spectrum and significant side effects
limit use to life-threatening infections or
after other drugs have failed. Meropenem
has a risk of seizures and is stable to
dehydropeptidase I.
aDVerse eFFects GI distress, rash, and CNS toxicity (seizures) at
high plasma levels.
mecHaNism oF resistaNce Inactivated by carbapenemases produced by,
eg, K pneumoniae, E coli, E aerogenes.
Monobactams Aztreonam
mecHaNism Less susceptible to β-lactamases. Prevents peptidoglycan cross-linking by binding to penicillin-
binding protein 3. Synergistic with aminoglycosides. No cross-allergenicity with penicillins.
cliNical Use Gram ⊝ rods only—no activity against gram ⊕ rods or anaerobes. For penicillin-allergic patients
and those with renal insufficiency who cannot tolerate aminoglycosides.
aDVerse eFFects Usually nontoxic; occasional GI upset.
Vancomycin
mecHaNism Inhibits cell wall peptidoglycan formation by binding D-Ala-D-Ala portion of cell wall precursors.
Bactericidal against most bacteria (bacteriostatic against C difficile). Not susceptible to
β-lactamases.
cliNical Use Gram ⊕ bugs only—for serious, multidrug-resistant organisms, including MRSA, S epidermidis,
sensitive Enterococcus species, and Clostridium difficile (oral dose for pseudomembranous colitis).
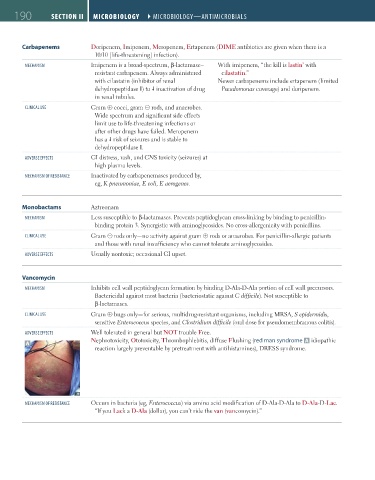
aDVerse eFFects Well tolerated in general but NOT trouble Free.
Nephrotoxicity, Ototoxicity, Thrombophlebitis, diffuse Flushing (red man syndrome A idiopathic
A
reaction largely preventable by pretreatment with antihistamines), DRESS syndrome.
mecHaNism oF resistaNce Occurs in bacteria (eg, Enterococcus) via amino acid modification of D-Ala-D-Ala to D-Ala-D-Lac.
“If you Lack a D-Ala (dollar), you can’t ride the van (vancomycin).”
FAS1_2019_03-Microbiology.indd 190 11/14/19 12:22 PM