Page 230 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 230
186 SEcTioN ii Microbiology ` microbiology—systems Microbiology ` microbiology—aNtimicrobials
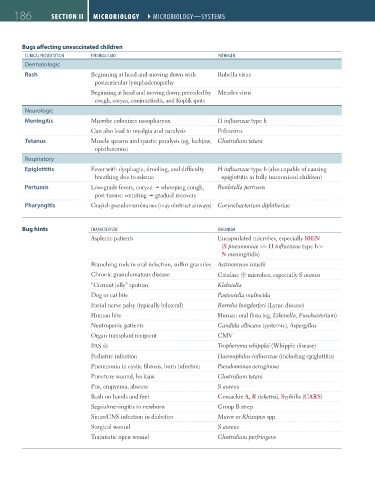
Bugs affecting unvaccinated children
cliNical PreseNtatioN FiNDiNgs/labs PatHogeN
Dermatologic
Rash Beginning at head and moving down with Rubella virus
postauricular lymphadenopathy
Beginning at head and moving down; preceded by Measles virus
cough, coryza, conjunctivitis, and Koplik spots
Neurologic
Meningitis Microbe colonizes nasopharynx H influenzae type b
Can also lead to myalgia and paralysis Poliovirus
Tetanus Muscle spasms and spastic paralysis (eg, lockjaw, Clostridium tetani
opisthotonus)
Respiratory
Epiglottitis Fever with dysphagia, drooling, and difficulty H influenzae type b (also capable of causing
breathing due to edema epiglottitis in fully immunized children)
Pertussis Low-grade fevers, coryza whooping cough, Bordetella pertussis
post-tussive vomiting gradual recovery
Pharyngitis Grayish pseudomembranes (may obstruct airways) Corynebacterium diphtheriae
Bug hints cHaracteristic orgaNism
Asplenic patients Encapsulated microbes, especially SHiN
(S pneumoniae >> H influenzae type b >
N meningitidis)
Branching rods in oral infection, sulfur granules Actinomyces israelii
Chronic granulomatous disease Catalase ⊕ microbes, especially S aureus
“Currant jelly” sputum Klebsiella
Dog or cat bite Pasteurella multocida
Facial nerve palsy (typically bilateral) Borrelia burgdorferi (Lyme disease)
Human bite Human oral flora (eg, Eikenella, Fusobacterium)
Neutropenic patients Candida albicans (systemic), Aspergillus
Organ transplant recipient CMV
PAS ⊕ Tropheryma whipplei (Whipple disease)
Pediatric infection Haemophilus influenzae (including epiglottitis)
Pneumonia in cystic fibrosis, burn infection Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Puncture wound, lockjaw Clostridium tetani
Pus, empyema, abscess S aureus
Rash on hands and feet Coxsackie A, R rickettsii, Syphilis (CARS)
Sepsis/meningitis in newborn Group B strep
Sinus/CNS infection in diabetics Mucor or Rhizopus spp.
Surgical wound S aureus
Traumatic open wound Clostridium perfringens
FAS1_2019_03-Microbiology.indd 186 11/14/19 12:22 PM