Page 248 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 248
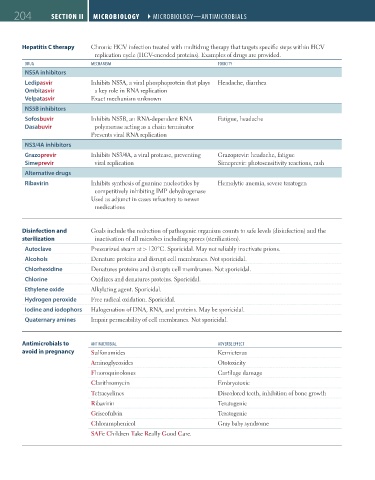
204 SEcTioN ii Microbiology ` microbiology—aNtimicrobials
Hepatitis C therapy Chronic HCV infection treated with multidrug therapy that targets specific steps within HCV
replication cycle (HCV-encoded proteins). Examples of drugs are provided.
DrUg mecHaNism toXicity
NS5A inhibitors
Ledipasvir Inhibits NS5A, a viral phosphoprotein that plays Headache, diarrhea
Ombitasvir a key role in RNA replication
Velpatasvir Exact mechanism unknown
NS5B inhibitors
Sofosbuvir Inhibits NS5B, an RNA-dependent RNA Fatigue, headache
Dasabuvir polymerase acting as a chain terminator
Prevents viral RNA replication
NS3/4A inhibitors
Grazoprevir Inhibits NS3/4A, a viral protease, preventing Grazoprevir: headache, fatigue
Simeprevir viral replication Simeprevir: photosensitivity reactions, rash
Alternative drugs
Ribavirin Inhibits synthesis of guanine nucleotides by Hemolytic anemia, severe teratogen
competitively inhibiting IMP dehydrogenase
Used as adjunct in cases refractory to newer
medications
Disinfection and Goals include the reduction of pathogenic organism counts to safe levels (disinfection) and the
sterilization inactivation of all microbes including spores (sterilization).
Autoclave Pressurized steam at > 120°C. Sporicidal. May not reliably inactivate prions.
Alcohols Denature proteins and disrupt cell membranes. Not sporicidal.
Chlorhexidine Denatures proteins and disrupts cell membranes. Not sporicidal.
Chlorine Oxidizes and denatures proteins. Sporicidal.
Ethylene oxide Alkylating agent. Sporicidal.
Hydrogen peroxide Free radical oxidation. Sporicidal.
Iodine and iodophors Halogenation of DNA, RNA, and proteins. May be sporicidal.
Quaternary amines Impair permeability of cell membranes. Not sporicidal.
Antimicrobials to aNtimicrobial aDVerse eFFect
avoid in pregnancy Sulfonamides Kernicterus
Aminoglycosides Ototoxicity
Fluoroquinolones Cartilage damage
Clarithromycin Embryotoxic
Tetracyclines Discolored teeth, inhibition of bone growth
Ribavirin Teratogenic
Griseofulvin Teratogenic
Chloramphenicol Gray baby syndrome
SAFe Children Take Really Good Care.
FAS1_2019_03-Microbiology.indd 204 11/14/19 12:22 PM