Page 367 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 367
CARDIOvASCuLAR ``CARdIOvASCulAR—PHARMACOlOGY CARDIOvASCuLAR ``CARdIOvASCulAR—PHARMACOlOGY SECTION III 323
Antiarrhythmics— Metoprolol, propranolol, esmolol, atenolol, timolol, carvedilol.
β-blockers (class II)
2+
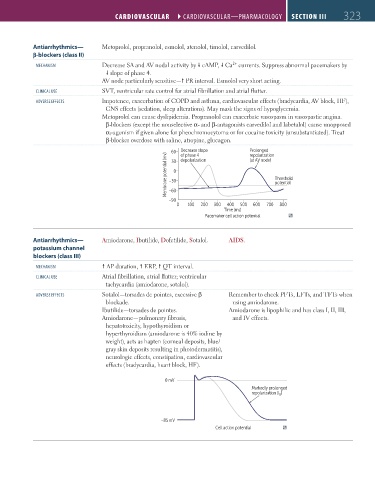
MECHANISM Decrease SA and AV nodal activity by cAMP, Ca currents. Suppress abnormal pacemakers by
slope of phase 4.
AV node particularly sensitive— PR interval. Esmolol very short acting.
ClINICAl uSE SVT, ventricular rate control for atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter.
AdvERSE EFFECTS Impotence, exacerbation of COPD and asthma, cardiovascular effects (bradycardia, AV block, HF),
CNS effects (sedation, sleep alterations). May mask the signs of hypoglycemia.
Metoprolol can cause dyslipidemia. Propranolol can exacerbate vasospasm in vasospastic angina.
β-blockers (except the nonselective α- and β-antagonists carvedilol and labetalol) cause unopposed
α 1 -agonism if given alone for pheochromocytoma or for cocaine toxicity (unsubstantiated). Treat
β-blocker overdose with saline, atropine, glucagon.
60 Decrease slope Prolonged
repolarization
of phase 4
Membrane potential (mv) –30 0 Threshold
depolarization
(at AV node)
30
potential
–60
–90
0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800
Time (ms)
Pacemaker cell action potential
Antiarrhythmics— Amiodarone, Ibutilide, Dofetilide, Sotalol. AIDS.
potassium channel
blockers (class III)
MECHANISM AP duration, ERP, QT interval.
ClINICAl uSE Atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter; ventricular
tachycardia (amiodarone, sotalol).
AdvERSE EFFECTS Sotalol—torsades de pointes, excessive β Remember to check PFTs, LFTs, and TFTs when
blockade. using amiodarone.
Ibutilide—torsades de pointes. Amiodarone is lipophilic and has class I, II, III,
Amiodarone—pulmonary fibrosis, and IV effects.
hepatotoxicity, hypothyroidism or
hyperthyroidism (amiodarone is 40% iodine by
weight), acts as hapten (corneal deposits, blue/
gray skin deposits resulting in photodermatitis),
neurologic effects, constipation, cardiovascular
effects (bradycardia, heart block, HF).
0 mV
Markedly prolonged
repolarization (I )
K
−85 mV
Cell action potential
FAS1_2019_07-Cardio.indd 323 11/7/19 4:24 PM