Page 368 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 368
324 SECTION III CARDIOvASCuLAR ``CARdIOvASCulAR—PHARMACOlOGY
Antiarrhythmics— Diltiazem, Verapamil
calcium channel
blockers (class IV)
MECHANISM Decrease conduction Velocity, ERP, PR interval.
ClINICAl uSE Prevention of nodal arrhythmias (eg, SVT), rate control in atrial fibrillation.
AdvERSE EFFECTS Constipation, flushing, edema, cardiovascular effects (HF, AV block, sinus node depression).
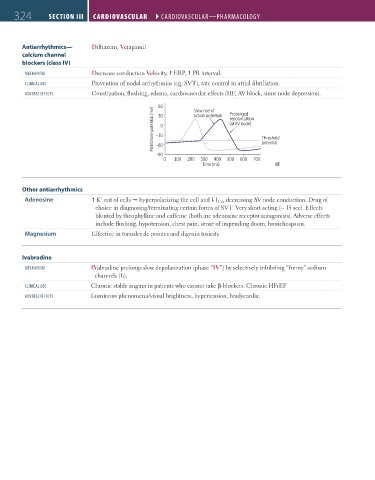
60 Slow rise of Prolonged
Membrane potential (mv) –30 0 repolarization Threshold
30
action potential
(at AV node)
–60
–90 potential
0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700
Time (ms)
Other antiarrhythmics
+
Adenosine K out of cells hyperpolarizing the cell and I Ca , decreasing AV node conduction. Drug of
choice in diagnosing/terminating certain forms of SVT. Very short acting (~ 15 sec). Effects
blunted by theophylline and caffeine (both are adenosine receptor antagonists). Adverse effects
include flushing, hypotension, chest pain, sense of impending doom, bronchospasm.
Magnesium Effective in torsades de pointes and digoxin toxicity.
Ivabradine
MECHANISM IVabradine prolongs slow depolarization (phase “IV”) by selectively inhibiting “funny” sodium
channels (I f ).
ClINICAl uSE Chronic stable angina in patients who cannot take β-blockers. Chronic HFrEF.
AdvERSE EFFECTS Luminous phenomena/visual brightness, hypertension, bradycardia.
FAS1_2019_07-Cardio.indd 324 11/7/19 4:24 PM