Page 404 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 404
360 seCtion iii Gastrointestinal ` gastrointestinal—anatomy Gastrointestinal ` gastrointestinal—anatomy
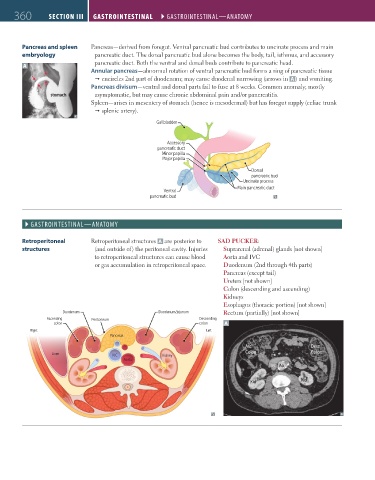
Pancreas and spleen Pancreas—derived from foregut. Ventral pancreatic bud contributes to uncinate process and main
embryology pancreatic duct. The dorsal pancreatic bud alone becomes the body, tail, isthmus, and accessory
pancreatic duct. Both the ventral and dorsal buds contribute to pancreatic head.
A
Annular pancreas—abnormal rotation of ventral pancreatic bud forms a ring of pancreatic tissue
encircles 2nd part of duodenum; may cause duodenal narrowing (arrows in A ) and vomiting.
Pancreas divisum—ventral and dorsal parts fail to fuse at 8 weeks. Common anomaly; mostly
stomach asymptomatic, but may cause chronic abdominal pain and/or pancreatitis.
Spleen—arises in mesentery of stomach (hence is mesodermal) but has foregut supply (celiac trunk
splenic artery).
Gallbladder
Accessory
pancreatic duct
Minor papilla
Major papilla
Dorsal
pancreatic bud
Uncinate process
Main pancreatic duct
Ventral
pancreatic bud
` gastrointestinal—anatomy
Retroperitoneal Retroperitoneal structures A are posterior to SAD PUCKER:
structures (and outside of) the peritoneal cavity. Injuries Suprarenal (adrenal) glands [not shown]
to retroperitoneal structures can cause blood Aorta and IVC
or gas accumulation in retroperitoneal space. Duodenum (2nd through 4th parts)
Pancreas (except tail)
Ureters [not shown]
Colon (descending and ascending)
Kidneys
Esophagus (thoracic portion) [not shown]
Duodenum Duodenum/jejunum Rectum (partially) [not shown]
Ascending Peritoneum Descending
colon colon A
Right Left
Pancreas
Asc Desc
Liver IVC Kidney Colon Colon
Aorta
IVC Ao
Kid Kid
FAS1_2019_09-Gastrointestinal.indd 360 11/7/19 4:42 PM