Page 407 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 407
Gastrointestinal ` gastrointestinal—anatomy Gastrointestinal ` gastrointestinal—anatomy seCtion iii 363
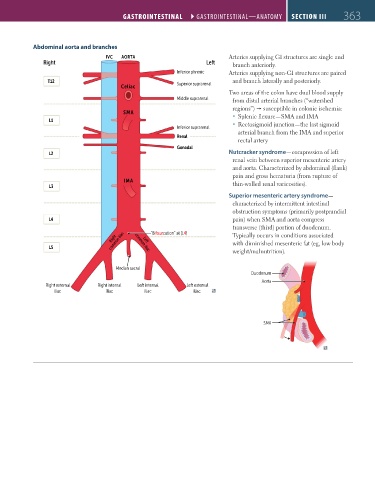
Abdominal aorta and branches
IVC AORTA Arteries supplying GI structures are single and
Right Left branch anteriorly.
Inferior phrenic Arteries supplying non-GI structures are paired
T12 Superior suprarenal and branch laterally and posteriorly.
Celiac
Two areas of the colon have dual blood supply
Middle suprarenal from distal arterial branches (“watershed
regions”) susceptible in colonic ischemia:
SMA Splenic flexure—SMA and IMA
L1 Rectosigmoid junction—the last sigmoid
Inferior suprarenal
arterial branch from the IMA and superior
Renal
rectal artery
Gonadal
L2 Nutcracker syndrome—compression of left
renal vein between superior mesenteric artery
and aorta. Characterized by abdominal (flank)
pain and gross hematuria (from rupture of
IMA
L3 thin-walled renal varicosities).
Superior mesenteric artery syndrome—
characterized by intermittent intestinal
obstruction symptoms (primarily postprandial
L4 pain) when SMA and aorta compress
transverse (third) portion of duodenum.
common iliac common iliac Typically occurs in conditions associated
“Bifourcation” at (L4)
Right
with diminished mesenteric fat (eg, low body
Left
L5 weight/malnutrition).
Median sacral
Duodenum
Aorta
Right external Right internal Left internal Left external
iliac iliac iliac iliac
SMA
FAS1_2019_09-Gastrointestinal.indd 363 11/7/19 4:42 PM