Page 420 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 420
376 seCtion iii Gastrointestinal ` gastrointestinal—PatHology Gastrointestinal ` gastrointestinal—PatHology
` gastrointestinal—PatHology
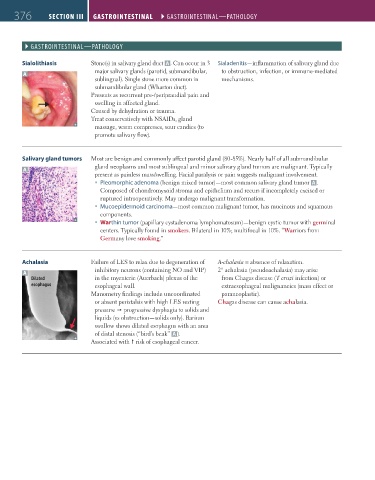
Sialolithiasis Stone(s) in salivary gland duct A. Can occur in 3 Sialadenitis—inflammation of salivary gland due
major salivary glands (parotid, submandibular, to obstruction, infection, or immune-mediated
A
sublingual). Single stone more common in mechanisms.
submandibular gland (Wharton duct).
Presents as recurrent pre-/periprandial pain and
swelling in affected gland.
Caused by dehydration or trauma.
Treat conservatively with NSAIDs, gland
massage, warm compresses, sour candies (to
promote salivary flow).
Salivary gland tumors Most are benign and commonly affect parotid gland (80-85%). Nearly half of all submandibular
A gland neoplasms and most sublingual and minor salivary gland tumors are malignant. Typically
present as painless mass/swelling. Facial paralysis or pain suggests malignant involvement.
Pleomorphic adenoma (benign mixed tumor)—most common salivary gland tumor A .
Composed of chondromyxoid stroma and epithelium and recurs if incompletely excised or
ruptured intraoperatively. May undergo malignant transformation.
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma—most common malignant tumor, has mucinous and squamous
components.
Warthin tumor (papillary cystadenoma lymphomatosum)—benign cystic tumor with germinal
centers. Typically found in smokers. Bilateral in 10%; multifocal in 10%. “Warriors from
Germany love smoking.”
Achalasia Failure of LES to relax due to degeneration of A-chalasia = absence of relaxation.
inhibitory neurons (containing NO and VIP) 2° achalasia (pseudoachalasia) may arise
A
Dilated in the myenteric (Auerbach) plexus of the from Chagas disease (T cruzi infection) or
esophagus esophageal wall. extraesophageal malignancies (mass effect or
Manometry findings include uncoordinated paraneoplastic).
or absent peristalsis with high LES resting Chagas disease can cause achalasia.
pressure progressive dysphagia to solids and
liquids (vs obstruction—solids only). Barium
swallow shows dilated esophagus with an area
of distal stenosis (“bird’s beak” A ).
Associated with risk of esophageal cancer.
FAS1_2019_09-Gastrointestinal.indd 376 11/7/19 4:42 PM