Page 418 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 418
374 seCtion iii Gastrointestinal ` gastrointestinal—PHysiology Gastrointestinal ` gastrointestinal—PHysiology
Vitamin and mineral absorption
Iron Absorbed as Fe in duodenum Iron Fist, Bro
2+
Folate Absorbed in small bowel Clinically relevant in patients with small bowel
disease or after resection (eg, vitamin B
Vitamin B Absorbed in terminal ileum along with bile 12
12 deficiency following terminal ileum resection)
salts, requires intrinsic factor
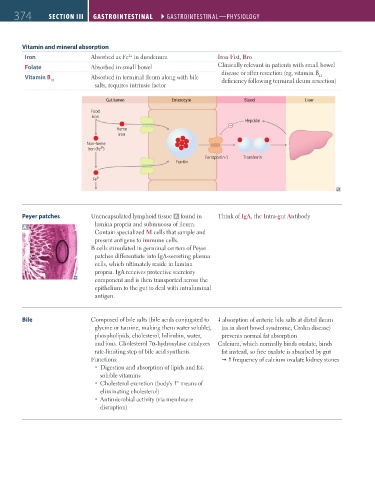
Gut lumen Enterocyte Blood Liver
Food
iron
Hepcidin
Heme
iron
Non-heme
iron (Fe³ ) +
Ferroportin-1 Transferrin
Ferritin
Fe² +
Peyer patches Unencapsulated lymphoid tissue A found in Think of IgA, the Intra-gut Antibody
A lamina propria and submucosa of ileum.
Contain specialized M cells that sample and
present antigens to immune cells.
B cells stimulated in germinal centers of Peyer
patches differentiate into IgA-secreting plasma
cells, which ultimately reside in lamina
propria. IgA receives protective secretory
component and is then transported across the
epithelium to the gut to deal with intraluminal
antigen.
Bile Composed of bile salts (bile acids conjugated to absorption of enteric bile salts at distal ileum
glycine or taurine, making them water soluble), (as in short bowel syndrome, Crohn disease)
phospholipids, cholesterol, bilirubin, water, prevents normal fat absorption
and ions. Cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase catalyzes Calcium, which normally binds oxalate, binds
rate-limiting step of bile acid synthesis. fat instead, so free oxalate is absorbed by gut
Functions: frequency of calcium oxalate kidney stones
Digestion and absorption of lipids and fat-
soluble vitamins
Cholesterol excretion (body’s 1° means of
eliminating cholesterol)
Antimicrobial activity (via membrane
disruption)
FAS1_2019_09-Gastrointestinal.indd 374 11/7/19 4:42 PM