Page 449 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 449
Hematology and oncology ` hematology and oncology—emBRyology Hematology and oncology ` hematology and oncology—emBRyology SectIon III 405
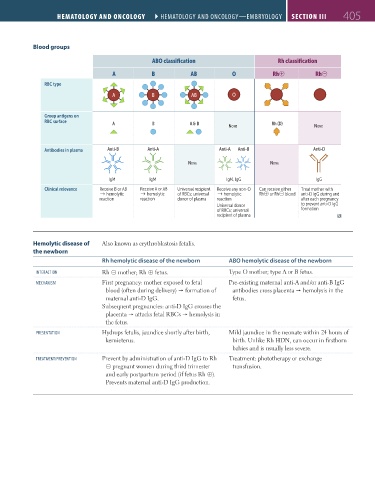
Blood groups
ABO classification Rh classification
A B AB O Rh Rh
RBC type
A B AB O
Group antigens on
RBC surface A B A & B Rh (D)
NONE NONE
Antibodies in plasma Anti-B Anti-A Anti-A Anti-B Anti-D
NONE NONE
IgM IgM IgM, IgG IgG
Clinical relevance Receive B or AB Receive A or AB Universal recipient Receive any non-O Can receive either Treat mother with
hemolytic hemolytic of RBCs; universal ↑ hemolytic Rh or Rh blood anti-D IgG during and
↑
↑
reaction reaction donor of plasma reaction after each pregnancy
Universal donor to prevent anti-D IgG
of RBCs; universal formation
recipient of plasma
Hemolytic disease of Also known as erythroblastosis fetalis.
the newborn
Rh hemolytic disease of the newborn ABO hemolytic disease of the newborn
InteRactIon Rh ⊝ mother; Rh ⊕ fetus. Type O mother; type A or B fetus.
mechanISm First pregnancy: mother exposed to fetal Pre-existing maternal anti-A and/or anti-B IgG
blood (often during delivery) formation of antibodies cross placenta hemolysis in the
maternal anti-D IgG. fetus.
Subsequent pregnancies: anti-D IgG crosses the
placenta attacks fetal RBCs hemolysis in
the fetus.
PReSentatIon Hydrops fetalis, jaundice shortly after birth, Mild jaundice in the neonate within 24 hours of
kernicterus. birth. Unlike Rh HDN, can occur in firstborn
babies and is usually less severe.
tReatment/PReVentIon Prevent by administration of anti-D IgG to Rh Treatment: phototherapy or exchange
⊝ pregnant women during third trimester transfusion.
and early postpartum period (if fetus Rh ⊕).
Prevents maternal anti-D IgG production.
FAS1_2019_10-HemaOncol.indd 405 11/7/19 5:04 PM