Page 452 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 452
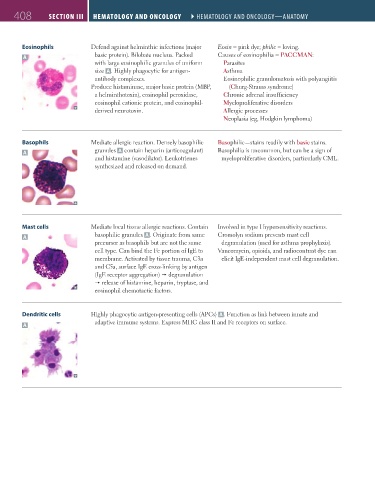
408 SectIon III Hematology and oncology ` hematology and oncology—anatomy Hematology and oncology ` hematology and oncology—anatomy
Eosinophils Defend against helminthic infections (major Eosin = pink dye; philic = loving.
A basic protein). Bilobate nucleus. Packed Causes of eosinophilia = PACCMAN:
with large eosinophilic granules of uniform Parasites
size A . Highly phagocytic for antigen- Asthma
antibody complexes. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis
Produce histaminase, major basic protein (MBP, (Churg-Strauss syndrome)
a helminthotoxin), eosinophil peroxidase, Chronic adrenal insufficiency
eosinophil cationic protein, and eosinophil- Myeloproliferative disorders
derived neurotoxin. Allergic processes
Neoplasia (eg, Hodgkin lymphoma)
Basophils Mediate allergic reaction. Densely basophilic Basophilic—stains readily with basic stains.
A granules A contain heparin (anticoagulant) Basophilia is uncommon, but can be a sign of
and histamine (vasodilator). Leukotrienes myeloproliferative disorders, particularly CML.
synthesized and released on demand.
Mast cells Mediate local tissue allergic reactions. Contain Involved in type I hypersensitivity reactions.
A basophilic granules A . Originate from same Cromolyn sodium prevents mast cell
precursor as basophils but are not the same degranulation (used for asthma prophylaxis).
cell type. Can bind the Fc portion of IgE to Vancomycin, opioids, and radiocontrast dye can
membrane. Activated by tissue trauma, C3a elicit IgE-independent mast cell degranulation.
and C5a, surface IgE cross-linking by antigen
(IgE receptor aggregation) degranulation
release of histamine, heparin, tryptase, and
eosinophil chemotactic factors.
Dendritic cells Highly phagocytic antigen-presenting cells (APCs) A . Function as link between innate and
A adaptive immune systems. Express MHC class II and Fc receptors on surface.
FAS1_2019_10-HemaOncol.indd 408 11/7/19 5:04 PM