Page 453 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 453
Hematology and oncology ` hematology and oncology—anatomy Hematology and oncology ` hematology and oncology—anatomy SectIon III 409
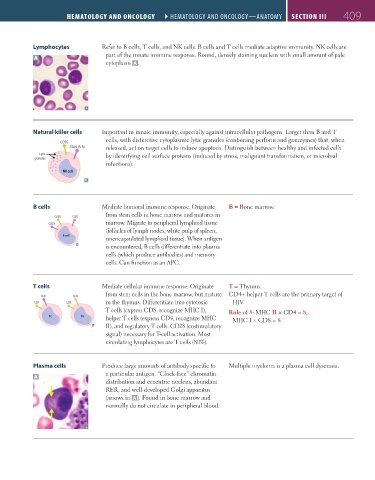
Lymphocytes Refer to B cells, T cells, and NK cells. B cells and T cells mediate adaptive immunity. NK cells are
part of the innate immune response. Round, densely staining nucleus with small amount of pale
A
cytoplasm A .
Natural killer cells Important in innate immunity, especially against intracellular pathogens. Larger than B and T
cells, with distinctive cytoplasmic lytic granules (containing perforin and granzymes) that, when
CD56
CD16 (FcR) released, act on target cells to induce apoptosis. Distinguish between healthy and infected cells
Lytic by identifying cell surface proteins (induced by stress, malignant transformation, or microbial
granules
infections).
NK cell
B cells Mediate humoral immune response. Originate B = Bone marrow.
from stem cells in bone marrow and matures in
CD20 CD21
marrow. Migrate to peripheral lymphoid tissue
CD19
(follicles of lymph nodes, white pulp of spleen,
B cell
unencapsulated lymphoid tissue). When antigen
is encountered, B cells differentiate into plasma
cells (which produce antibodies) and memory
cells. Can function as an APC.
T cells Mediate cellular immune response. Originate T = Thymus.
from stem cells in the bone marrow, but mature CD4+ helper T cells are the primary target of
CD8 CD4
CD3 CD3 in the thymus. Differentiate into cytotoxic HIV.
T cells (express CD8, recognize MHC I), Rule of 8: MHC II × CD4 = 8;
Tc Th helper T cells (express CD4, recognize MHC MHC I × CD8 = 8.
II), and regulatory T cells. CD28 (costimulatory
signal) necessary for T-cell activation. Most
circulating lymphocytes are T cells (80%).
Plasma cells Produce large amounts of antibody specific to Multiple myeloma is a plasma cell dyscrasia.
A a particular antigen. “Clock-face” chromatin
distribution and eccentric nucleus, abundant
RER, and well-developed Golgi apparatus
(arrows in A ). Found in bone marrow and
normally do not circulate in peripheral blood.
FAS1_2019_10-HemaOncol.indd 409 11/7/19 5:04 PM