Page 534 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 534
490 SecTioN iii Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—embryology Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—embryology
` neurology—embryology
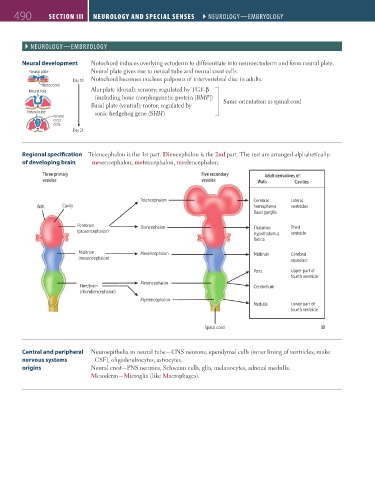
Neural development Notochord induces overlying ectoderm to differentiate into neuroectoderm and form neural plate.
Neural plate Neural plate gives rise to neural tube and neural crest cells.
Day 18 Notochord becomes nucleus pulposus of intervertebral disc in adults.
Notochord
Neural fold Alar plate (dorsal): sensory; regulated by TGF-β
(including bone morphogenetic protein [BMP]) Same orientation as spinal cord
Basal plate (ventral): motor; regulated by
Neural tube sonic hedgehog gene (SHH)
Neural
crest
cells
Day 21
Regional specification Telencephalon is the 1st part. Diencephalon is the 2nd part. The rest are arranged alphabetically:
of developing brain mesencephalon, metencephalon, myelencephalon.
Three primary Five secondary Adult derivatives of:
vesicles vesicles Walls Cavities
Telencephalon Cerebral Lateral
Wall Cavity hemispheres ventricles
Basal ganglia
Forebrain Diencephalon Thalamus Third
(prosencephalon)
Hypothalamus ventricle
Retina
Midbrain Mesencephalon Midbrain Cerebral
(mesencephalon)
aqueduct
Pons Upper part of
fourth ventricle
Metencephalon
Hindbrain Cerebellum
(rhombencephalon)
Myelencephalon
Medulla Lower part of
fourth ventricle
Spinal cord
Central and peripheral Neuroepithelia in neural tube—CNS neurons, ependymal cells (inner lining of ventricles, make
nervous systems CSF), oligodendrocytes, astrocytes.
origins Neural crest—PNS neurons, Schwann cells, glia, melanocytes, adrenal medulla.
Mesoderm—Microglia (like Macrophages).
FAS1_2019_12-Neurol.indd 490 11/8/19 7:39 AM