Page 535 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 535
Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—embryology Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—embryology SecTioN iii 491
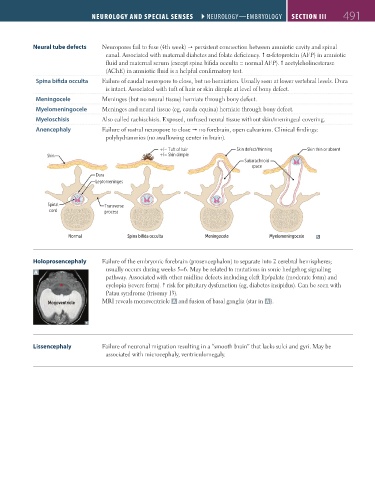
Neural tube defects Neuropores fail to fuse (4th week) persistent connection between amniotic cavity and spinal
canal. Associated with maternal diabetes and folate deficiency. α-fetoprotein (AFP) in amniotic
fluid and maternal serum (except spina bifida occulta = normal AFP). acetylcholinesterase
(AChE) in amniotic fluid is a helpful confirmatory test.
Spina bifida occulta Failure of caudal neuropore to close, but no herniation. Usually seen at lower vertebral levels. Dura
is intact. Associated with tuft of hair or skin dimple at level of bony defect.
Meningocele Meninges (but no neural tissue) herniate through bony defect.
Myelomeningocele Meninges and neural tissue (eg, cauda equina) herniate through bony defect.
Myeloschisis Also called rachischisis. Exposed, unfused neural tissue without skin/meningeal covering.
Anencephaly Failure of rostral neuropore to close no forebrain, open calvarium. Clinical findings:
polyhydramnios (no swallowing center in brain).
+/− Tuft of hair Skin defect/thinning Skin thin or absent
Skin +/− Skin dimple
Subarachnoid
space
Dura
Leptomeninges
Spinal Transverse
cord process
Normal Spina bifida occulta Meningocele Myelomeningocele
Holoprosencephaly Failure of the embryonic forebrain (prosencephalon) to separate into 2 cerebral hemispheres;
usually occurs during weeks 5–6. May be related to mutations in sonic hedgehog signaling
A
pathway. Associated with other midline defects including cleft lip/palate (moderate form) and
★ cyclopia (severe form). risk for pituitary dysfunction (eg, diabetes insipidus). Can be seen with
Patau syndrome (trisomy 13).
Monoventricle MRI reveals monoventricle A and fusion of basal ganglia (star in A ).
Lissencephaly Failure of neuronal migration resulting in a “smooth brain” that lacks sulci and gyri. May be
associated with microcephaly, ventriculomegaly.
FAS1_2019_12-Neurol.indd 491 11/8/19 7:39 AM