Page 537 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 537
Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—embryology Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—AnAtomy And Physiology SecTioN iii 493
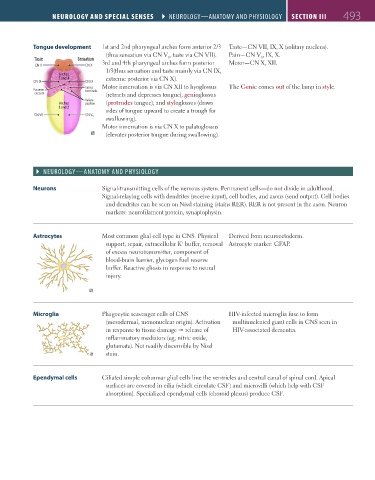
Tongue development 1st and 2nd pharyngeal arches form anterior 2/3 Taste—CN VII, IX, X (solitary nucleus).
(thus sensation via CN V , taste via CN VII). Pain—CN V , IX, X.
3
3
Taste Sensation 3rd and 4th pharyngeal arches form posterior Motor—CN X, XII.
CN X CN X
1/3(thus sensation and taste mainly via CN IX,
Arches
3 and 4 extreme posterior via CN X).
CN IX CN IX
Sulcus Motor innervation is via CN XII to hyoglossus The Genie comes out of the lamp in style.
Foramen terminalis
caecum (retracts and depresses tongue), genioglossus
Vallate
Arches papillae (protrudes tongue), and styloglossus (draws
1 and 2
sides of tongue upward to create a trough for
CN VII CN V₃
swallowing).
Motor innervation is via CN X to palatoglossus
(elevates posterior tongue during swallowing).
` neurology—AnAtomy And Physiology
Neurons Signal-transmitting cells of the nervous system. Permanent cells—do not divide in adulthood.
Signal-relaying cells with dendrites (receive input), cell bodies, and axons (send output). Cell bodies
and dendrites can be seen on Nissl staining (stains RER). RER is not present in the axon. Neuron
markers: neurofilament protein, synaptophysin.
Astrocytes Most common glial cell type in CNS. Physical Derived from neuroectoderm.
support, repair, extracellular K buffer, removal Astrocyte marker: GFAP.
+
of excess neurotransmitter, component of
blood-brain barrier, glycogen fuel reserve
buffer. Reactive gliosis in response to neural
injury.
Microglia Phagocytic scavenger cells of CNS HIV-infected microglia fuse to form
(mesodermal, mononuclear origin). Activation multinucleated giant cells in CNS seen in
in response to tissue damage release of HIV-associated dementia.
inflammatory mediators (eg, nitric oxide,
glutamate). Not readily discernible by Nissl
stain.
Ependymal cells Ciliated simple columnar glial cells line the ventricles and central canal of spinal cord. Apical
surfaces are covered in cilia (which circulate CSF) and microvilli (which help with CSF
absorption). Specialized ependymal cells (choroid plexus) produce CSF.
FAS1_2019_12-Neurol.indd 493 11/8/19 7:39 AM