Page 622 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 622
578 SeCTIOn III Renal ` RENAL—EmbRyoLogy Renal ` RENAL—EmbRyoLogy
` RENAL—EmbRyoLogy
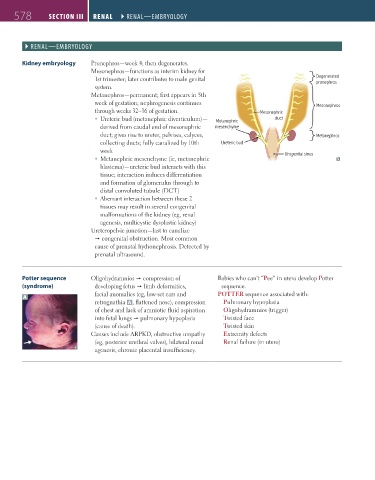
Kidney embryology Pronephros—week 4; then degenerates.
Mesonephros—functions as interim kidney for
1st trimester; later contributes to male genital Degenerated
pronephros
system.
Metanephros—permanent; first appears in 5th
week of gestation; nephrogenesis continues Mesonephros
through weeks 32–36 of gestation. Mesonephric
Ureteric bud (metanephric diverticulum)— Metanephric duct
derived from caudal end of mesonephric mesenchyme
duct; gives rise to ureter, pelvises, calyces, Metanephros
collecting ducts; fully canalized by 10th Ureteric bud
week Ur
Urogenital sinusogenital sinus
Metanephric mesenchyme (ie, metanephric
blastema)—ureteric bud interacts with this
tissue; interaction induces differentiation
and formation of glomerulus through to
distal convoluted tubule (DCT)
Aberrant interaction between these 2
tissues may result in several congenital
malformations of the kidney (eg, renal
agenesis, multicystic dysplastic kidney)
Ureteropelvic junction—last to canalize
congenital obstruction. Most common
cause of prenatal hydronephrosis. Detected by
prenatal ultrasound.
Potter sequence Oligohydramnios compression of Babies who can’t “Pee” in utero develop Potter
(syndrome) developing fetus limb deformities, sequence.
A facial anomalies (eg, low-set ears and POTTER sequence associated with:
retrognathia A , flattened nose), compression Pulmonary hypoplasia
of chest and lack of amniotic fluid aspiration Oligohydramnios (trigger)
into fetal lungs pulmonary hypoplasia Twisted face
(cause of death). Twisted skin
Causes include ARPKD, obstructive uropathy Extremity defects
(eg, posterior urethral valves), bilateral renal Renal failure (in utero)
agenesis, chronic placental insufficiency.
FAS1_2019_14-Renal.indd 578 11/7/19 5:42 PM