Page 625 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 625
Renal ` RENAL—ANAtomy Renal ` RENAL—PhysioLogy SeCTIOn III 581
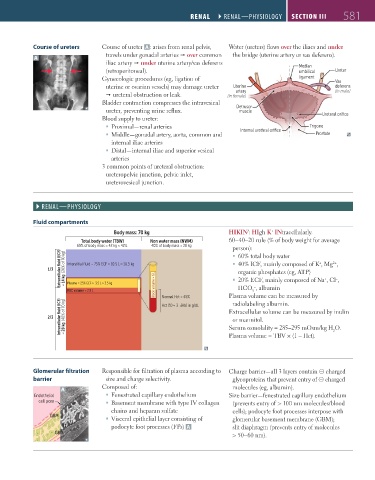
Course of ureters Course of ureter A : arises from renal pelvis, Water (ureters) flows over the iliacs and under
travels under gonadal arteries over common the bridge (uterine artery or vas deferens).
A
iliac artery under uterine artery/vas deferens
(retroperitoneal). Median Ureter
umbilical
Gynecologic procedures (eg, ligation of ligament Vas
uterine or ovarian vessels) may damage ureter Uterine deferens
artery
ureteral obstruction or leak. (in female) (in male)
Bladder contraction compresses the intravesical
ureter, preventing urine reflux. Detrusor
muscle
Blood supply to ureter: Ureteral orifice
Proximal—renal arteries Trigone
Middle—gonadal artery, aorta, common and Internal urethral orifice Prostate
internal iliac arteries
Distal—internal iliac and superior vesical
arteries
3 common points of ureteral obstruction:
ureteropelvic junction, pelvic inlet,
ureterovesical junction.
` RENAL—PhysioLogy
Fluid compartments
+
Body mass: 70 kg HIKIN’: HIgh K INtracellularly.
Total body water (TBW) Non water mass (NWM) 60–40–20 rule (% of body weight for average
60% of body mass = 42 kg ≈ 42 L 40% of body mass = 28 kg person):
60% total body water
+
2+
1/3 Extracellular fluid (ECF) ~ 14 kg (20% of 70 kg) Interstitial fluid = 75% ECF ≈ 10.5 L ≈ 10.5 kg 40% ICF, mainly composed of K , Mg ,
organic phosphates (eg, ATP)
20% ECF, mainly composed of Na , Cl ,
–
+
Plasma = 25% ECF ≈ 3.5 L ≈ 3.5 kg
HCO , albumin
–
RBC volume ≈ 2.8 L Blood volume ≈ 6 L Normal Hct = 45% Plasma volume can be measured by
3
radiolabeling albumin.
Extracellular volume can be measured by inulin
2/3 Intracellular fluid (ICF) ~ 28 kg (40% of 70 kg) Hct (%) ≈ 3 [Hb] in g/dL Plasma volume = TBV × (1 – Hct). 2
or mannitol.
Serum osmolality = 285–295 mOsm/kg H O.
Glomerular filtration Responsible for filtration of plasma according to Charge barrier—all 3 layers contain ⊝ charged
barrier size and charge selectivity. glycoproteins that prevent entry of ⊝ charged
A Composed of: molecules (eg, albumin).
Endothelial Fenestrated capillary endothelium Size barrier—fenestrated capillary endothelium
cell pore Basement membrane with type IV collagen (prevents entry of > 100 nm molecules/blood
chains and heparan sulfate cells); podocyte foot processes interpose with
GBM Visceral epithelial layer consisting of glomerular basement membrane (GBM);
FP
FP podocyte foot processes (FPs) A slit diaphragm (prevents entry of molecules
GBM > 50–60 nm).
FAS1_2019_14-Renal.indd 581 11/7/19 5:42 PM