Page 657 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 657
RepRoductive ` REPRODUCTIVE—EmbRyOlOgy RepRoductive ` REPRODUCTIVE—EmbRyOlOgy SectioN iii 613
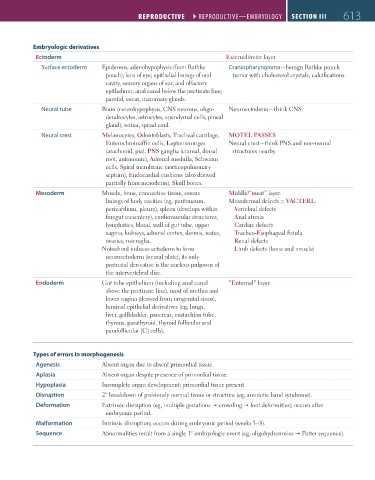
Embryologic derivatives
Ectoderm External/outer layer
Surface ectoderm Epidermis; adenohypophysis (from Rathke Craniopharyngioma—benign Rathke pouch
pouch); lens of eye; epithelial linings of oral tumor with cholesterol crystals, calcifications.
cavity, sensory organs of ear, and olfactory
epithelium; anal canal below the pectinate line;
parotid, sweat, mammary glands.
Neural tube Brain (neurohypophysis, CNS neurons, oligo- Neuroectoderm—think CNS.
dendrocytes, astrocytes, ependymal cells, pineal
gland), retina, spinal cord.
Neural crest Melanocytes, Odontoblasts, Tracheal cartilage, MOTEL PASSES
Enterochromaffin cells, Leptomeninges Neural crest—think PNS and non-neural
(arachnoid, pia), PNS ganglia (cranial, dorsal structures nearby.
root, autonomic), Adrenal medulla, Schwann
cells, Spiral membrane (aorticopulmonary
septum), Endocardial cushions (also derived
partially from mesoderm), Skull bones.
Mesoderm Muscle, bone, connective tissue, serous Middle/“meat” layer.
linings of body cavities (eg, peritoneum, Mesodermal defects = VACTERL:
pericardium, pleura), spleen (develops within Vertebral defects
foregut mesentery), cardiovascular structures, Anal atresia
lymphatics, blood, wall of gut tube, upper Cardiac defects
vagina, kidneys, adrenal cortex, dermis, testes, Tracheo-Esophageal fistula
ovaries, microglia. Renal defects
Notochord induces ectoderm to form Limb defects (bone and muscle)
neuroectoderm (neural plate); its only
postnatal derivative is the nucleus pulposus of
the intervertebral disc.
Endoderm Gut tube epithelium (including anal canal “Enternal” layer.
above the pectinate line), most of urethra and
lower vagina (derived from urogenital sinus),
luminal epithelial derivatives (eg, lungs,
liver, gallbladder, pancreas, eustachian tube,
thymus, parathyroid, thyroid follicular and
parafollicular [C] cells).
Types of errors in morphogenesis
Agenesis Absent organ due to absent primordial tissue.
Aplasia Absent organ despite presence of primordial tissue.
Hypoplasia Incomplete organ development; primordial tissue present.
Disruption 2° breakdown of previously normal tissue or structure (eg, amniotic band syndrome).
Deformation Extrinsic disruption (eg, multiple gestations crowding foot deformities); occurs after
embryonic period.
Malformation Intrinsic disruption; occurs during embryonic period (weeks 3–8).
Sequence Abnormalities result from a single 1° embryologic event (eg, oligohydramnios Potter sequence).
FAS1_2019_15-Repro.indd 613 11/7/19 5:52 PM