Page 658 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 658
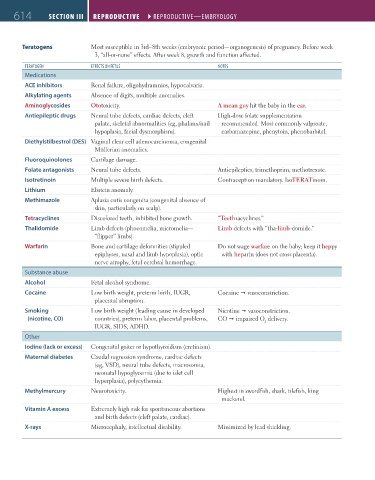
614 SectioN iii RepRoductive ` REPRODUCTIVE—EmbRyOlOgy RepRoductive ` REPRODUCTIVE—EmbRyOlOgy
Teratogens Most susceptible in 3rd–8th weeks (embryonic period—organogenesis) of pregnancy. Before week
3, “all-or-none” effects. After week 8, growth and function affected.
TERATOgEN EFFECTS ON FETUS NOTES
Medications
ACE inhibitors Renal failure, oligohydramnios, hypocalvaria.
Alkylating agents Absence of digits, multiple anomalies.
Aminoglycosides Ototoxicity. A mean guy hit the baby in the ear.
Antiepileptic drugs Neural tube defects, cardiac defects, cleft High-dose folate supplementation
palate, skeletal abnormalities (eg, phalanx/nail recommended. Most commonly valproate,
hypoplasia, facial dysmorphism). carbamazepine, phenytoin, phenobarbital.
Diethylstilbestrol (DES) Vaginal clear cell adenocarcinoma, congenital
Müllerian anomalies.
Fluoroquinolones Cartilage damage.
Folate antagonists Neural tube defects. Antiepileptics, trimethoprim, methotrexate.
Isotretinoin Multiple severe birth defects. Contraception mandatory. IsoTERATinoin.
Lithium Ebstein anomaly.
Methimazole Aplasia cutis congenita (congenital absence of
skin, particularly on scalp).
Tetracyclines Discolored teeth, inhibited bone growth. “Teethracyclines.”
Thalidomide Limb defects (phocomelia, micromelia— Limb defects with “tha-limb-domide.”
“flipper” limbs).
Warfarin Bone and cartilage deformities (stippled Do not wage warfare on the baby; keep it heppy
epiphyses, nasal and limb hypoplasia), optic with heparin (does not cross placenta).
nerve atrophy, fetal cerebral hemorrhage.
Substance abuse
Alcohol Fetal alcohol syndrome.
Cocaine Low birth weight, preterm birth, IUGR, Cocaine vasoconstriction.
placental abruption.
Smoking Low birth weight (leading cause in developed Nicotine vasoconstriction.
(nicotine, CO) countries), preterm labor, placental problems, CO impaired O delivery.
2
IUGR, SIDS, ADHD.
Other
Iodine (lack or excess) Congenital goiter or hypothyroidism (cretinism).
Maternal diabetes Caudal regression syndrome, cardiac defects
(eg, VSD), neural tube defects, macrosomia,
neonatal hypoglycemia (due to islet cell
hyperplasia), polycythemia.
Methylmercury Neurotoxicity. Highest in swordfish, shark, tilefish, king
mackerel.
Vitamin A excess Extremely high risk for spontaneous abortions
and birth defects (cleft palate, cardiac).
X-rays Microcephaly, intellectual disability. Minimized by lead shielding.
FAS1_2019_15-Repro.indd 614 11/7/19 5:52 PM