Page 674 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 674
630 SectioN iii RepRoductive ` REPRODUCTIVE—PHySIOlOgy RepRoductive ` REPRODUCTIVE—PHySIOlOgy
Estrogen
SOURCE Ovary (17β-estradiol), placenta (estriol), adipose Potency: estradiol > estrone > estriol.
tissue (estrone via aromatization).
FUNCTION Development of genitalia and breast, female fat Pregnancy:
distribution. 50-fold in estradiol and estrone
Growth of follicle, endometrial proliferation, 1000-fold in estriol (indicator of fetal well-
myometrial excitability. being)
Upregulation of estrogen, LH, and progesterone Estrogen receptors expressed in cytoplasm;
receptors; feedback inhibition of FSH and translocate to nucleus when bound by
LH, then LH surge; stimulation of prolactin estrogen.
secretion.
transport proteins, SHBG; HDL; LDL.
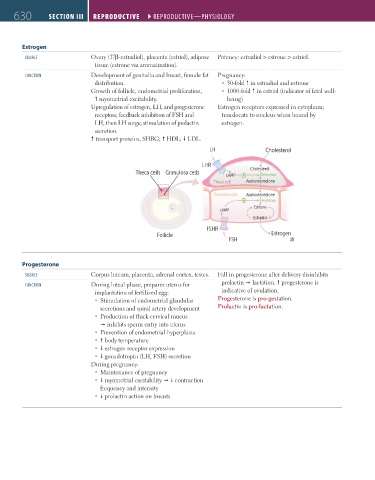
LH Cholesterol
LHR
Theca cells Granulosa cells Cholesterol
cAMP Desmolase
Theca cell Androstenedione
Granulosa cell Androstenedione
Aromatase
Estrone
cAMP
Estradiol
FSHR
Follicle Estrogen
FSH
Progesterone
SOURCE Corpus luteum, placenta, adrenal cortex, testes. Fall in progesterone after delivery disinhibits
FUNCTION During luteal phase, prepares uterus for prolactin lactation. progesterone is
implantation of fertilized egg: indicative of ovulation.
Stimulation of endometrial glandular Progesterone is pro-gestation.
secretions and spiral artery development Prolactin is pro-lactation.
Production of thick cervical mucus
inhibits sperm entry into uterus
Prevention of endometrial hyperplasia
body temperature
estrogen receptor expression
gonadotropin (LH, FSH) secretion
During pregnancy:
Maintenance of pregnancy
myometrial excitability contraction
frequency and intensity
prolactin action on breasts
FAS1_2019_15-Repro.indd 630 11/7/19 5:52 PM