Page 677 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 677
RepRoductive ` REPRODUCTIVE—PHySIOlOgy RepRoductive ` REPRODUCTIVE—PHySIOlOgy SectioN iii 633
Abnormal uterine Characterized as either heavy menstrual Terms such as dysfunctional uterine bleeding,
bleeding bleeding (AUB/HMB) or intermenstrual menorrhagia, oligomenorrhea are no longer
bleeding (AUB/IMB). recommended.
These are further subcategorized by PALM-
COEIN:
Structural causes (PALM): Polyp,
Adenomyosis, Leiomyoma, or Malignancy/
hyperplasia
Non-structural causes (COEIN):
Coagulopathy, Ovulatory, Endometrial,
Iatrogenic, Not yet classified
Pregnancy Fertilization most commonly occurs in upper
end of fallopian tube (the ampulla). Occurs
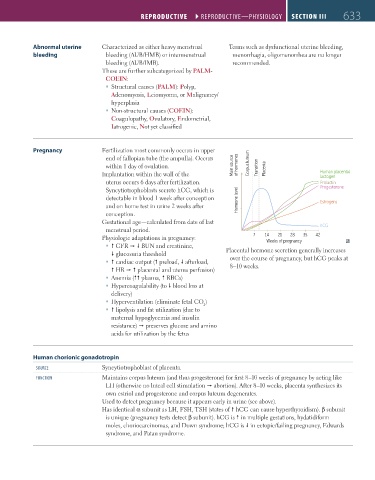
within 1 day of ovulation. Main source of hormones Corpus luteum Transition Placenta
Implantation within the wall of the Human placental
lactogen
uterus occurs 6 days after fertilization. Prolactin
Syncytiotrophoblasts secrete hCG, which is Progesterone
detectable in blood 1 week after conception Hormone level
and on home test in urine 2 weeks after Estrogens
conception.
Gestational age—calculated from date of last
menstrual period. hCG
21
28
Physiologic adaptations in pregnancy: 7 14 Weeks of pregnancy 35 42
GFR BUN and creatinine,
glucosuria threshold Placental hormone secretion generally increases
cardiac output ( preload, afterload, over the course of pregnancy, but hCG peaks at
HR placental and uterus perfusion) 8–10 weeks.
Anemia ( plasma, RBCs)
Hypercoagulability (to blood loss at
delivery)
Hyperventilation (eliminate fetal CO )
2
lipolysis and fat utilization (due to
maternal hypoglycemia and insulin
resistance) preserves glucose and amino
acids for utilization by the fetus
Human chorionic gonadotropin
SOURCE Syncytiotrophoblast of placenta.
FUNCTION Maintains corpus luteum (and thus progesterone) for first 8–10 weeks of pregnancy by acting like
LH (otherwise no luteal cell stimulation abortion). After 8–10 weeks, placenta synthesizes its
own estriol and progesterone and corpus luteum degenerates.
Used to detect pregnancy because it appears early in urine (see above).
Has identical α subunit as LH, FSH, TSH (states of hCG can cause hyperthyroidism). β subunit
is unique (pregnancy tests detect β subunit). hCG is in multiple gestations, hydatidiform
moles, choriocarcinomas, and Down syndrome; hCG is in ectopic/failing pregnancy, Edwards
syndrome, and Patau syndrome.
FAS1_2019_15-Repro.indd 633 11/7/19 5:52 PM