Page 82 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 82
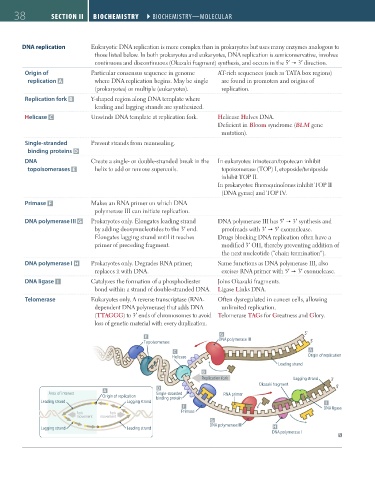
38 SECTION II BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—MOlECUlAR BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—MOlECUlAR
DNA replication Eukaryotic DNA replication is more complex than in prokaryotes but uses many enzymes analogous to
those listed below. In both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, DNA replication is semiconservative, involves
continuous and discontinuous (Okazaki fragment) synthesis, and occurs in the 5′ 3′ direction.
Origin of Particular consensus sequence in genome AT-rich sequences (such as TATA box regions)
replication A where DNA replication begins. May be single are found in promoters and origins of
(prokaryotes) or multiple (eukaryotes). replication.
Replication fork B Y-shaped region along DNA template where
leading and lagging strands are synthesized.
Helicase C Unwinds DNA template at replication fork. Helicase Halves DNA.
Deficient in Bloom syndrome (BLM gene
mutation).
Single-stranded Prevent strands from reannealing.
binding proteins D
DNA Create a single- or double-stranded break in the In eukaryotes: irinotecan/topotecan inhibit
topoisomerases E helix to add or remove supercoils. topoisomerase (TOP) I, etoposide/teniposide
inhibit TOP II.
In prokaryotes: fluoroquinolones inhibit TOP II
(DNA gyrase) and TOP IV.
Primase F Makes an RNA primer on which DNA
polymerase III can initiate replication.
DNA polymerase III G Prokaryotes only. Elongates leading strand DNA polymerase III has 5′ 3′ synthesis and
by adding deoxynucleotides to the 3′ end. proofreads with 3′ 5′ exonuclease.
Elongates lagging strand until it reaches Drugs blocking DNA replication often have a
primer of preceding fragment. modified 3′ OH, thereby preventing addition of
the next nucleotide (“chain termination”).
DNA polymerase I H Prokaryotes only. Degrades RNA primer; Same functions as DNA polymerase III, also
replaces it with DNA. excises RNA primer with 5′ 3′ exonuclease.
DNA ligase I Catalyzes the formation of a phosphodiester Joins Okazaki fragments.
bond within a strand of double-stranded DNA. Ligase Links DNA.
Telomerase Eukaryotes only. A reverse transcriptase (RNA- Often dysregulated in cancer cells, allowing
dependent DNA polymerase) that adds DNA unlimited replication.
(TTAGGG) to 3′ ends of chromosomes to avoid Telomerase TAGs for Greatness and Glory.
loss of genetic material with every duplication.
E G 3'
Topoisomerase DNA polymerase III 5'
C A
Helicase Origin of replication
Leading strand
B
Replication fork Lagging strand 3'
Okazaki fragment
D 5'
A
Area of interest Single-stranded RNA primer
Origin of replication binding protein
Leading strand Lagging strand I
F DNA ligase
Primase
Fork Fork
movement movement
G
DNA polymerase III
Lagging strand Leading strand H
DNA polymerase I
FAS1_2019_01-Biochem.indd 38 11/7/19 3:16 PM