Page 86 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 86
42 SECTION II BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—MOlECUlAR BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—MOlECUlAR
RNA polymerases
Eukaryotes RNA polymerase I makes rRNA, the most I, II, and III are numbered in the same order
common (rampant) type; present only in that their products are used in protein
nucleolus. synthesis: rRNA, mRNA, then tRNA.
RNA polymerase II makes mRNA (massive), α-amanitin, found in Amanita phalloides (death
microRNA (miRNA), and small nuclear RNA cap mushrooms), inhibits RNA polymerase II.
(snRNA). Causes severe hepatotoxicity if ingested.
RNA polymerase III makes 5S rRNA, tRNA Actinomycin D, also called dactinomycin,
(tiny). inhibits RNA polymerase in both prokaryotes
No proofreading function, but can initiate and eukaryotes.
chains. RNA polymerase II opens DNA at
promoter site.
Prokaryotes 1 RNA polymerase (multisubunit complex) Rifampin inhibits DNA-dependent RNA
makes all 3 kinds of RNA. polymerase in prokaryotes.
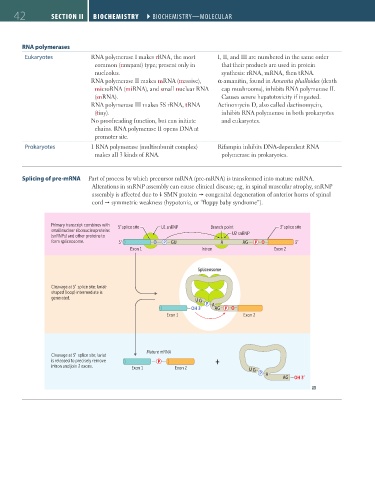
Splicing of pre-mRNA Part of process by which precursor mRNA (pre-mRNA) is transformed into mature mRNA.
Alterations in snRNP assembly can cause clinical disease; eg, in spinal muscular atrophy, snRNP
assembly is affected due to SMN protein congenital degeneration of anterior horns of spinal
cord symmetric weakness (hypotonia, or “floppy baby syndrome”).
Primary transcript combines with 5 splice site U1 snRNP Branch point 3 splice site
small nuclear ribonucleoproteins
(snRNPs) and other proteins to U2 snRNP
form spliceosome. 5 O P GU A AG P O 3
Exon 1 Intron Exon 2
Spliceosome
Cleavage at 5 splice site; lariat-
shaped (loop) intermediate is
generated.
U G
P A
OH 3 AG P O
Exon 1 Exon 2
Mature mRNA
Cleavage at 3 splice site; lariat
is released to precisely remove P +
intron and join 2 exons. Exon 1 Exon 2 U G
P A
AG OH 3
FAS1_2019_01-Biochem.indd 42 11/7/19 3:16 PM