Page 33 - The City and Guilds Textbook: Plumbing Book 1 for the Level 3 Apprenticeship (9189), Level 2 Technical Certificate (8202) and Level 2 Diploma (6035)
P. 33
Chapter 1 Health and safety practices and systems
Table 1.4 Classifications of hazardous substances
Category Description Example
Toxic Cyanide, asbestos, lead Poisons and dangerous substances
that have the ability to cause death
if ingested, inhaled or absorbed into
the body.
Harmful Fluxes, solvents, cleaning fluids, Harmful substances could be in any
chemicals, dust form, liquid, solid (dust particles) or
gas.
Corrosive Hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid, Such substances have the ability to
caustic soda cause severe burns to exposed parts
of the body.
Irritant Fibreglass roof insulation, some Can cause irritation of the skin, eyes,
paints, solvents and sealants nose and throat.
Oxidising Oxygen from welding bottles Materials are induced to burn
fiercely by adding oxygen to a fire.
Extremely Petrol, LPG, acetylene gas, solvent These have the potential to burn
flammable weld adhesives and cleaning agents fiercely if the substance is either
exposed to a source of ignition
or subjected to temperatures
close to its flashpoint, so that it
spontaneously combusts.
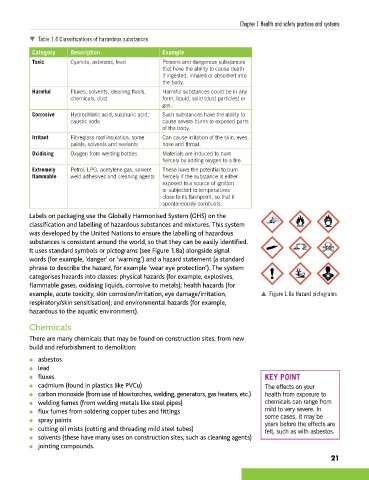
Labels on packaging use the Globally Harmonised System (GHS) on the
classification and labelling of hazardous substances and mixtures. This system
was developed by the United Nations to ensure the labelling of hazardous
substances is consistent around the world, so that they can be easily identified.
It uses standard symbols or pictograms (see Figure 1.8a) alongside signal
words (for example, ‘danger’ or ‘warning’) and a hazard statement (a standard
phrase to describe the hazard, for example ‘wear eye protection’). The system
categorises hazards into classes: physical hazards (for example, explosives,
flammable gases, oxidising liquids, corrosive to metals); health hazards (for
example, acute toxicity, skin corrosion/irritation, eye damage/irritation, p Figure 1.8a Hazard pictograms
respiratory/skin sensitisation); and environmental hazards (for example,
hazardous to the aquatic environment).
Chemicals
There are many chemicals that may be found on construction sites, from new
build and refurbishment to demolition:
● asbestos
● lead
● fluxes KEY POINT
● cadmium (found in plastics like PVCu) The effects on your
● carbon monoxide (from use of blowtorches, welding, generators, gas heaters, etc.) health from exposure to
● welding fumes (from welding metals like steel pipes) chemicals can range from
● flux fumes from soldering copper tubes and fittings mild to very severe. In
● spray paints some cases, it may be
years before the effects are
● cutting oil mists (cutting and threading mild steel tubes) felt, such as with asbestos.
● solvents (these have many uses on construction sites, such as cleaning agents)
● jointing compounds.
21
9781510416482.indb 21 29/03/19 8:49 PM