Page 563 - The City and Guilds Textbook: Plumbing Book 1 for the Level 3 Apprenticeship (9189), Level 2 Technical Certificate (8202) and Level 2 Diploma (6035)
P. 563
Chapter 9 Sanitation systems
The primary ventilated stack is probably the most common system installed in
domestic dwellings. It relies on all the appliances being closely grouped around
the stack and therefore does not need an extra ventilating stack like other
systems. It is used in situations where the discharge stack is large enough to
limit pressure fluctuations without the need for a separate ventilating stack.
Waste pipe sizes and lengths
Waste pipes need to fall away from the appliances with enough of a fall for the
water to reach what is known as a ‘self-cleansing velocity’. The fall is known as
the gradient.
Table 9.1 shows the size of waste pipe for a given appliance installed on a
primary ventilating stack, and its maximum length and gradient.
Table 9.1 Branch and waste pipe sizes, gradients and trap seal depths
Appliance Pipe size (mm) Max. length (m) Gradient (mm/m) Trap seal depth (mm)
A WC branch 75–100 6 18 50
18–22
B Washbasin and bidet 32 1.7 75
(see Figure 9.2)
C Washing machine/dishwasher 40 3 18–90 75
D Bath 40 3 18–90 50
E Kitchen/utility sink 40 3 18–90 75
Where these lengths are exceeded, then the next pipe size up should be used; 40 mm appliances will need to increase to
50 mm pipe, the length and gradient of which are listed below.
Appliances with 50 mm waste pipe 4 18–90 75
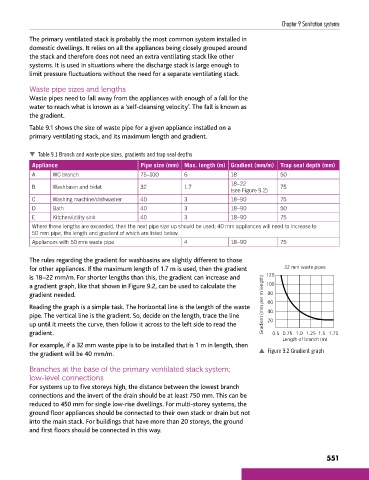
The rules regarding the gradient for washbasins are slightly different to those
for other appliances. If the maximum length of 1.7 m is used, then the gradient 32 mm waste pipes
is 18–22 mm/m. For shorter lengths than this, the gradient can increase and 120
a gradient graph, like that shown in Figure 9.2, can be used to calculate the 100
gradient needed. 80
Reading the graph is a simple task. The horizontal line is the length of the waste Gradient (mm per m length) 60
pipe. The vertical line is the gradient. So, decide on the length, trace the line 40
up until it meets the curve, then follow it across to the left side to read the 20
gradient. 0.5 0.75 1.0 1.25 1.5 1.75
Length of branch (m)
For example, if a 32 mm waste pipe is to be installed that is 1 m in length, then
the gradient will be 40 mm/m. p Figure 9.2 Gradient graph
Branches at the base of the primary ventilated stack system:
low-level connections
For systems up to five storeys high, the distance between the lowest branch
connections and the invert of the drain should be at least 750 mm. This can be
reduced to 450 mm for single low-rise dwellings. For multi-storey systems, the
ground floor appliances should be connected to their own stack or drain but not
into the main stack. For buildings that have more than 20 storeys, the ground
and first floors should be connected in this way.
551
9781510416482.indb 551 29/03/19 9:05 PM