Page 635 - The City and Guilds Textbook: Plumbing Book 1 for the Level 3 Apprenticeship (9189), Level 2 Technical Certificate (8202) and Level 2 Diploma (6035)
P. 635
Chapter 10 Domestic fuel systems
Natural gas
Natural gas is a combustible mixture of hydrocarbon gases and is probably the
most widely used hydrocarbon fuel on Earth. It is colourless and odourless in its
purest form and, when it is combusted, it releases a vast amount of energy with
fewer emissions than many other common fossil fuels. Natural gas is naturally
occurring and is usually found during the extraction of oil from deep below the
Earth’s surface, but it can also be found near coal formations and seams.
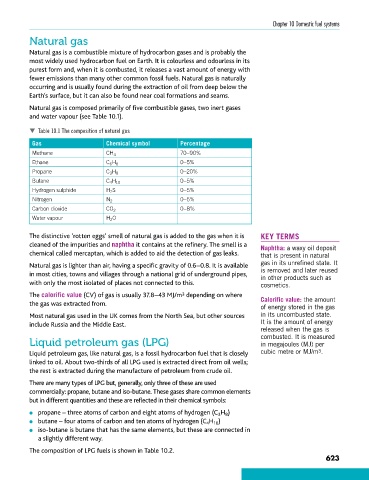
Natural gas is composed primarily of five combustible gases, two inert gases
and water vapour (see Table 10.1).
Table 10.1 The composition of natural gas
Gas Chemical symbol Percentage
Methane CH 4 70–90%
Ethane C 6 H 6 0–5%
Propane C 3 H 8 0–20%
Butane C 4 H 10 0–5%
Hydrogen sulphide H 2 S 0–5%
Nitrogen N 2 0–5%
Carbon dioxide CO 2 0–8%
Water vapour H 2 O
The distinctive ‘rotten eggs’ smell of natural gas is added to the gas when it is KEY TERMS
cleaned of the impurities and naphtha it contains at the refinery. The smell is a Naphtha: a waxy oil deposit
chemical called mercaptan, which is added to aid the detection of gas leaks. that is present in natural
Natural gas is lighter than air, having a specific gravity of 0.6–0.8. It is available gas in its unrefined state. It
in most cities, towns and villages through a national grid of underground pipes, is removed and later reused
in other products such as
with only the most isolated of places not connected to this. cosmetics.
3
The calorific value (CV) of gas is usually 37.8–43 MJ/m depending on where Calorific value: the amount
the gas was extracted from. of energy stored in the gas
Most natural gas used in the UK comes from the North Sea, but other sources in its uncombusted state.
include Russia and the Middle East. It is the amount of energy
released when the gas is
combusted. It is measured
Liquid petroleum gas (LPG) in megajoules (MJ) per
3
Liquid petroleum gas, like natural gas, is a fossil hydrocarbon fuel that is closely cubic metre or MJ/m .
linked to oil. About two-thirds of all LPG used is extracted direct from oil wells;
the rest is extracted during the manufacture of petroleum from crude oil.
There are many types of LPG but, generally, only three of these are used
commercially: propane, butane and iso-butane. These gases share common elements
but in different quantities and these are reflected in their chemical symbols:
l propane – three atoms of carbon and eight atoms of hydrogen (C H )
8
3
l butane – four atoms of carbon and ten atoms of hydrogen (C H )
4 10
l iso-butane is butane that has the same elements, but these are connected in
a slightly different way.
The composition of LPG fuels is shown in Table 10.2.
623
9781510416482.indb 623 29/03/19 9:08 PM