Page 639 - The City and Guilds Textbook: Plumbing Book 1 for the Level 3 Apprenticeship (9189), Level 2 Technical Certificate (8202) and Level 2 Diploma (6035)
P. 639
Chapter 10 Domestic fuel systems
Sustainable, low-carbon fuels
Low carbon can be classified as fuels made from renewable sources like those
described below.
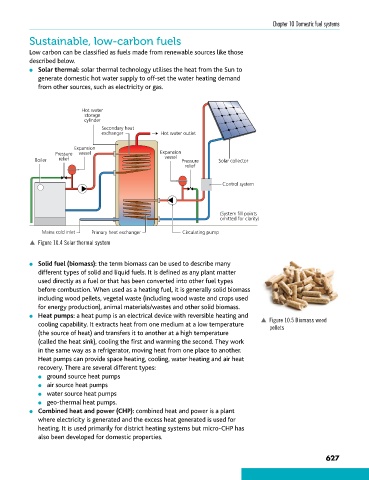
l Solar thermal: solar thermal technology utilises the heat from the Sun to
generate domestic hot water supply to off-set the water heating demand
from other sources, such as electricity or gas.
Hot water
storage
cylinder
Secondary heat
exchanger Hot water outlet
Expansion
Pressure vessel Expansion
Boiler relief vessel Pressure Solar collector
relief
Control system
(System fill points
omitted for clarity)
Mains cold inlet Primary heat exchanger Circulating pump
p Figure 10.4 Solar thermal system
l Solid fuel (biomass): the term biomass can be used to describe many
different types of solid and liquid fuels. It is defined as any plant matter
used directly as a fuel or that has been converted into other fuel types
before combustion. When used as a heating fuel, it is generally solid biomass
including wood pellets, vegetal waste (including wood waste and crops used
for energy production), animal materials/wastes and other solid biomass.
l Heat pumps: a heat pump is an electrical device with reversible heating and
cooling capability. It extracts heat from one medium at a low temperature p Figure 10.5 Biomass wood
pellets
(the source of heat) and transfers it to another at a high temperature
(called the heat sink), cooling the first and warming the second. They work
in the same way as a refrigerator, moving heat from one place to another.
Heat pumps can provide space heating, cooling, water heating and air heat
recovery. There are several different types:
l ground source heat pumps
l air source heat pumps
l water source heat pumps
l geo-thermal heat pumps.
l Combined heat and power (CHP): combined heat and power is a plant
where electricity is generated and the excess heat generated is used for
heating. It is used primarily for district heating systems but micro-CHP has
also been developed for domestic properties.
627
9781510416482.indb 627 29/03/19 9:08 PM