Page 270 - APPLIED PROCESS DESIGN FOR CHEMICAL AND PETROCHEMICAL PLANTS, Volume 1, 3rd Edition
P. 270
240 Applied Process Design for Chemical and Petrochemical Plants
for assumed spherical particles in a surfactant-free system The minimum residence time as determined by
[26]. The minimum particle diameter for many fine dis- Stokes' Law terminal settling velocity is:
persions is 100 microns; however, Reference [28] has
reviewed a wide variety of liquid drop data and suggests
that a good choice is 150 micron or 0.15 cm or 0.0005 ft. tmin = b /v., min (4-17)
This is also the particle size used in the API Design Manu-
al [24]. Using too large an assumed particle diameter will he = height of segment of circle, in.
cause the settler unit to become unreasonably small.
vt = terminal settling velocity, in./min
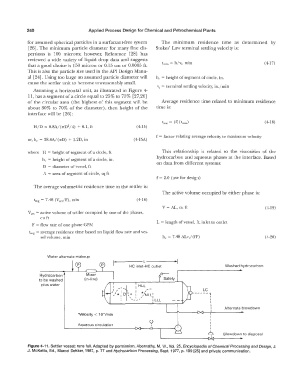
Assuming a horizontal unit, as illustrated in Figure 4-
11, has a segment ofa circle equal to 25% to 75% [27,26]
of the circular area (the highest of this segment will be Average residence time related to minimum residence
about 30% to 70% of the diameter), then height of the time is:
interface will be [26]:
( 4-18)
H/D = 0.8A/(7iD 2 /4) + 0.1, ft (4-15)
f = factor relating average velocity to maximum velocity
or, he = 38.4A/ ( TID) + l.20, in (4-15A)
where H = height of segment of a circle, fl This relationship is related to the viscosities of the
hydrocarbon and aqueous phases at the interface. Based
he = height of segment of a circle, in.
on data from different systems:
D = diameter of vessel, ft
A = area of segment of circle, sq ft
f = 2.0 (use for design)
The average volumetric residence time in the settler is:
The active volume occupied by either phase is:
la,g = 7.48 (VseJF), min ( 4-16)
V = AL, cu ft ( 4-19)
Vw = active volume of settler occupied by one of the phases,
cu ft
L = length of vessel, ft, inlet to outlet
F = flow rate of one phase GPM
lavg = average residence time based on liquid flow rate and ves-
sel volume, min he = 7.48 ALvJ (ff) ( 4-20)
Water alternate makeup
------L------
.. HC inlet-HG outlet Washed hydrocarbon
Hydrocarbon Mixer <}--
to be washed (in-line) Safety
plus water
LC
-----,
I
I
I
i
I Alternate blowdown
*Velocity< 10"/min
Q
Aqueous circulation I
Blowdown to disposal
Figure 4-11. Settler vessel; runs full. Adapted by permission, Abernathy, M. W., Vol. 25, Encyclopedia of Chemical Processing and Design, J.
J. McKetta, Ed., Marcel Dekker, 1987, p. 77 and Hydrocarbon Processing, Sept.1977, p.199 [25] and private communication.