Page 148 - Template Tesis UTM v2.0
P. 148
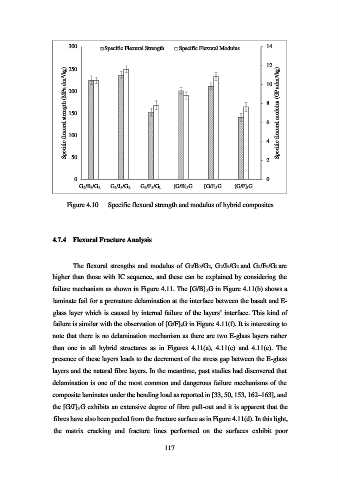
300 Specific Flexural Strength Specific Flexural Modulus 14
12
250
Specific flexural strength (MPa.dm 3 /kg) 200 8 Specific flexural modulus (GPa.dm 3 /kg)
10
150
6
100
4
50
2
0 0
G2/B3/G2 G2/J3/G2 G2/F3/G2 [G/B]3G [G/J]3G [G/F]3G
Figure 4.10 Specific flexural strength and modulus of hybrid composites
4.7.4 Flexural Fracture Analysis
The flexural strengths and modulus of G2/B3/G2, G2/J3/G2 and G2/F3/G2 are
higher than those with IC sequence, and these can be explained by considering the
failure mechanism as shown in Figure 4.11. The [G/B]3G in Figure 4.11(b) shows a
laminate fail for a premature delamination at the interface between the basalt and E-
glass layer which is caused by internal failure of the layers’ interface. This kind of
failure is similar with the observation of [G/F]3G in Figure 4.11(f). It is interesting to
note that there is no delamination mechanism as there are two E-glass layers rather
than one in all hybrid structures as in Figures 4.11(a), 4.11(c) and 4.11(e). The
presence of these layers leads to the decrement of the stress gap between the E-glass
layers and the natural fibre layers. In the meantime, past studies had discovered that
delamination is one of the most common and dangerous failure mechanisms of the
composite laminates under the bending load as reported in [33, 50, 153, 162–163], and
the [G/J]3G exhibits an extensive degree of fibre pull-out and it is apparent that the
fibres have also been peeled from the fracture surface as in Figure 4.11(d). In this light,
the matrix cracking and fracture lines performed on the surfaces exhibit poor
117