Page 8 - Spotlight A+ Physics Form 4.5
P. 8
Form
4 Physics Chapter 3 Gravitation
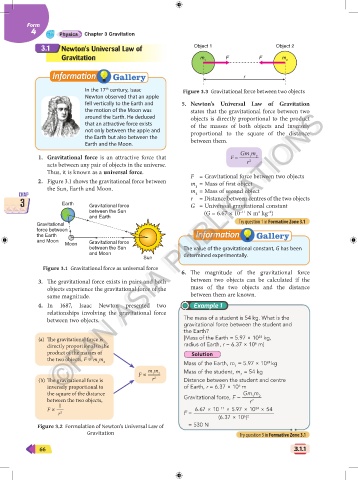
3.1 Newton's Universal Law of Object 1 Object 2
Gravitation m 1 F F m 2
r
In the 17 century, Isaac Figure 3.3 Gravitational force between two objects
th
Newton observed that an apple
fell vertically to the Earth and 5. Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation
the motion of the Moon was states that the gravitational force between two
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
around the Earth. He deduced objects is directly proportional to the product
that an attractive force exists of the masses of both objects and inversely
not only between the apple and proportional to the square of the distance
the Earth but also between the
Earth and the Moon. between them.
Gm m
1. Gravitational force is an attractive force that F = 1 2 2
acts between any pair of objects in the universe. r
Thus, it is known as a universal force. F = Gravitational force between two objects
2. Figure 3.1 shows the gravitational force between m = Mass of first object
1
the Sun, Earth and Moon. m = Mass of second object
CHAP r = Distance between centres of the two objects
2
3 Earth Gravitational force G = Universsal gravitational constant
between the Sun (G = 6.67 × 10 N m kg )
–2
–11
2
and Earth
Try question 1 in Formative Zone 3.1
Gravitational
force between
the Earth
and Moon Gravitational force
Moon
between the Sun The value of the gravitational constant, G has been
and Moon determined experimentally.
Sun
Figure 3.1 Gravitational force as universal force
6. The magnitude of the gravitational force
3. The gravitational force exists in pairs and both between two objects can be calculated if the
objects experience the gravitational force of the mass of the two objects and the distance
same magnitude. between them are known.
4. In 1687, Isaac Newton presented two Example 1
relationships involving the gravitational force
between two objects. The mass of a student is 54 kg. What is the
gravitational force between the student and
the Earth?
24
(a) The gravitational force is [Mass of the Earth = 5.97 × 10 kg,
6
directly proportional to the radius of Earth, r = 6.37 × 10 m]
product of the masses of Solution
the two objects, F ∝ m m
24
1 2 Mass of the Earth, m = 5.97 × 10 kg
1
m m Mass of the student, m = 54 kg
F ∝ 1 2 2
(b) The gravitational force is r 2 Distance between the student and centre
6
inversely proportional to of Earth, r = 6.37 × 10 m
the square of the distance Gm m 2
1
between the two objects, Gravitational force, F = r 2
1
24
−11
F ∝ 6.67 × 10 × 5.97 × 10 × 54
r 2 F =
6 2
(6.37 × 10 )
Figure 3.2 Formulation of Newton’s Universal Law of = 530 N
Gravitation Try question 3 in Formative Zone 3.1
66 3.1.1