Page 12 - Spotlight A+ Physics Form 4.5
P. 12
Form
4
Chapter 4 Heat Physics
Relationship between Pressure and Volume of a Gas
4.4
Inference: The volume of a gas affects the pressure of the gas.
Hypothesis: The smaller the volume of a gas, the higher the pressure of the gas.
Aim: To determine the relationship between the volume and pressure of a fixed mass of gas at a constant
temperature.
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
Variables:
(a) Manipulated : Volume, V
(b) Responding : Pressure, P
(c) Constant : Temperature and mass of air
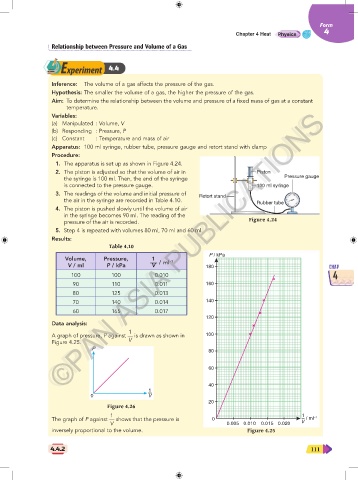
Apparatus: 100 ml syringe, rubber tube, pressure gauge and retort stand with clamp
Procedure:
1. The apparatus is set up as shown in Figure 4.24.
2. The piston is adjusted so that the volume of air in Piston
the syringe is 100 ml. Then, the end of the syringe Pressure gauge
is connected to the pressure gauge. 100 ml syringe
3. The readings of the volume and initial pressure of Retort stand
the air in the syringe are recorded in Table 4.10.
Rubber tube
4. The piston is pushed slowly until the volume of air
in the syringe becomes 90 ml. The reading of the
pressure of the air is recorded. Figure 4.24
5. Step 4 is repeated with volumes 80 ml, 70 ml and 60 ml.
Results:
Table 4.10
P / kPa
Volume, Pressure, 1 –1
V / ml P / kPa V / ml 180 CHAP
100 100 0.010 4
90 110 0.011 160
80 125 0.013
70 140 0.014 140
60 165 0.017
120
Data analysis:
1
A graph of pressure, P against is drawn as shown in 100
Figure 4.25. V
P
80
60
40
1
—
0 V
Figure 4.26 20
1 1
The graph of P against shows that the pressure is 0 – / ml –1
V 0.005 0.010 0.015 0.020 V
inversely proportional to the volume. Figure 4.25
4.4.2 111