Page 21 - 1202 Question Bank Chemistry Form 4 KSSM
P. 21
26. B Sulphuric acid is a strong diprotic 44. B Fine salt dissolves faster. There is 0.02 (ii)
acid. It has the highest concentration g of salt per 1 cm of water in A but
3
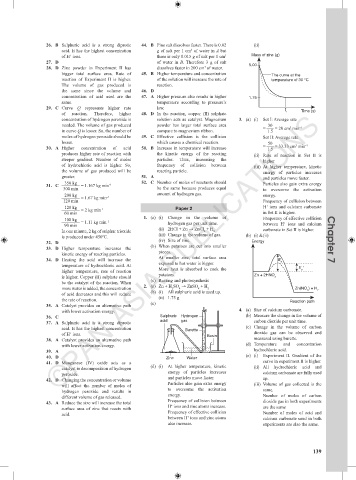
of H ions. there is only 0.015 g of salt per 1 cm 3 Mass of zinc (g)
+
27. D of water in B. Therefore 3 g of salt
28. D Zinc powder in Experiment II has dissolves faster in 200 cm of water. 5.00
3
bigger total surface area. Rate of 45. B Higher temperature and concentration The curve at the
reaction of Experiment II is higher. of the solution will increase the rate of temperature of 30 °C
The volume of gas produced is reaction.
the same since the volume and 46. D
concentration of acid used are the 47. A Higher pressure also results in higher 1.75
same. temperature according to pressure’s
29. C Curve Q represents higher rate law.
of reaction. Therefore, higher 48. D In the reaction, copper (II) sulphate t 1 Time (s)
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
concentration of hydrogen peroxide is solution acts as catalyst. Magnesium 3. (a) (i) Set I: Average rate
needed. The volume of gas produced powder has larger total surface area 30 3 –1
in curve Q is lesser. So, the number of compare to magnesium ribbon. = 1.5 = 20 cm min
moles of hydrogen peroxide should be 49. C Effective collision is the collision Set II: Average rate
lesser. which causes a chemical reaction. 50
3
30. A Higher concentration of acid 50. B Increase in temperature will increase = 1.5 = 33.33 cm min –1
produces higher rate of reaction with the kinetic energy of the reacting (ii) Rate of reaction in Set II is
steeper gradient. Number of moles particles. Thus, increasing the higher
of hydrochloric acid is higher. So, frequency of collision between (iii) At higher temperature, kinetic
the volume of gas produced will be reacting particle. energy of particles increases
greater. 51. A and particles move faster.
350 kg 52. C Number of moles of reactants should Particles also gain extra energy
31. C = 1.167 kg min –1
300 min be the same because produces equal to overcome the activation
200 kg = 1.67 kg min –1 amount of hydrogen gas. energy.
120 min Frequency of collision between
+
120 kg = 2 kg min –1 Paper 2 H ions and calcium carbonate
60 min in Set II is higher.
100 kg = 1.11 kg min –1 1. (a) (i) Change in the volume of Frequency of effective collision
+
90 min hydrogen gas per unit time. between H ions and calcium
In one minute, 2 kg of sulphur trioxide (ii) 2HCl + Zn → ZnCl + H 2 carbonate in Set II is higher.
2
is produced under 450ºC. (iii) Change in the volume of gas. (b) (i) & (ii)
32. D (iv) Size of zinc Energy Chapter 7
33. D Higher temperature increases the (b) When potatoes are cut into smaller
kinetic energy of reacting particles. pieces.
34. D Heating the acid will increase the At smaller size, total surface area E a
temperature of hydrochloric acid. At exposed to hot water is bigger. E '
higher temperature, rate of reaction More heat is absorbed to cook the a
is higher. Copper (II) sulphate should potatoes. Zn + 2HNO 3
be the catalyst of the reaction. When (c) Rusting and photosynthesis
more water is added, the concentration 2. (a) Zn + H SO → ZnSO + H 2 Zn(NO ) + H 2
2
4
4
3
of acid decreases and this will reduce (b) (i) All sulphuric acid is used up.
the rate of reaction. (ii) 1.75 g Reaction path
35. A Catalyst provides an alternative path (c)
with lower activation energy. 4. (a) Size of calcium carbonate.
36. C Sulphuric Hydrogen (b) Measure the change in the volume of
37. A Sulphuric acid is a strong diprotic acid gas carbon dioxide per unit time.
acid. It has the highest concentration Burette (c) Change in the volume of carbon
+
of H ions. Basin dioxide gas can be observed and
38. A Catalyst provides an alternative path measured using burette.
with lower activation energy. (d) Temperature and concentration
39. A hydrochloric acid.
40. D Zinc Water (e) (i) Experiment II. Gradient of the
41. D Manganese (IV) oxide acts as a curve in experiment II is higher.
catalyst in decomposition of hydrogen (d) (i) At higher temperature, kinetic (ii) All hydrochloric acid and
peroxide. energy of particles increases calcium carbonate are fully used
42. D Changing the concentration or volume and particles move faster. up.
will affect the number of moles of Particles also gain extra energy (iii) Volume of gas collected is the
hydrogen peroxide and results in to overcome the activation same.
different volume of gas released. energy. Number of moles of carbon
43. A Reduce the size will increase the total Frequency of collision between dioxide gas in both experiments
+
surface area of zinc that reacts with H ions and zinc atoms increase. are the same
acid. Frequency of effective collision Number of moles of acid and
+
between H ions and zinc atoms calcium carbonate used in both
also increase. experiments are also the same.
139