Page 19 - 1202 Question Bank Chemistry Form 4 KSSM
P. 19
PAPER 3
You are required to compare the electrical conductivity of molten X and molten Y.
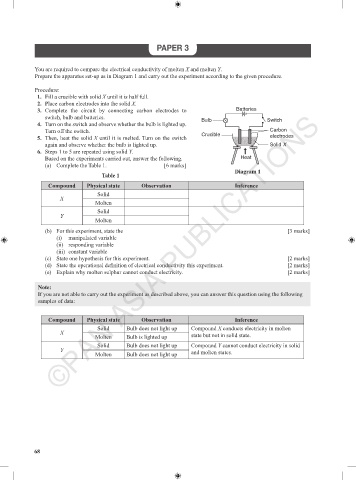
Prepare the apparatus set-up as in Diagram 1 and carry out the experiment according to the given procedure.
Procedure:
1. Fill a crucible with solid X until it is half full.
2. Place carbon electrodes into the solid X.
3. Complete the circuit by connecting carbon electrodes to Batteries
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
switch, bulb and batteries.
4. Turn on the switch and observe whether the bulb is lighted up. Bulb Switch
Turn off the switch. Carbon
5. Then, heat the solid X until it is melted. Turn on the switch Crucible electrodes
again and observe whether the bulb is lighted up. Solid X
6. Steps 1 to 5 are repeated using solid Y.
Based on the experiments carried out, answer the following. Heat
(a) Complete the Table 1. [6 marks]
Diagram 1
Table 1
Compound Physical state Observation Inference
Solid
X
Molten
Solid
Y
Molten
(b) For this experiment, state the [3 marks]
(i) manipulated variable
(ii) responding variable
(iii) constant variable
(c) State one hypothesis for this experiment. [2 marks]
(d) State the operational definition of electrical conductivity this experiment. [2 marks]
(e) Explain why molten sulphur cannot conduct electricity. [2 marks]
Note:
If you are not able to carry out the experiment as described above, you can answer this question using the following
samples of data:
Compound Physical state Observation Inference
Solid Bulb does not light up Compound X conducts electricity in molten
X
Molten Bulb is lighted up state but not in solid state.
Solid Bulb does not light up Compound Y cannot conduct electricity in solid
Y and molten states.
Molten Bulb does not light up
68