Page 4 - 1202 Question Bank Physics Form 5
P. 4
MUST
KNOW Important Facts
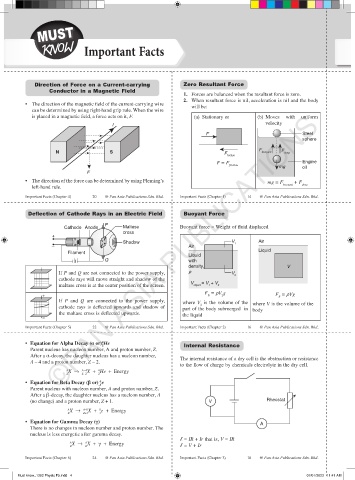
Direction of Force on a Current-carrying Zero Resultant Force
Conductor in a Magnetic Field
1. Forces are balanced when the resultant force is zero.
2. When resultant force is nil, acceleration is nil and the body
• The direction of the magnetic field of the current-carrying wire
will be:
can be determined by using right-hand grip rule. When the wire
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
is placed in a magnetic field, a force acts on it, F. (a) Stationary or (b) Moves with uniform
velocity
I
F Steel
sphere
F F
N S F buoyant drag
friction
F = F Engine
friction mg oil
F
• The direction of the force can be determined by using Fleming’s mg = F + F
left-hand rule. buoyant drag
Important Facts (Chapter 4) 20 @ Pan Asia Publications Sdn. Bhd. Important Facts (Chapter 1) 14 @ Pan Asia Publications Sdn. Bhd.
Deflection of Cathode Rays in an Electric Field Buoyant Force
P
Cathode Anode Maltese Buoyant force = Weight of fluid displaced
cross
+
Shadow V 1 Air
– Air
Liquid
Filament
Liquid
Q with
density, V
If P and Q are not connected to the power supply, ρ V
2
cathode rays will move straight and shadow of the
maltase cross is at the center position of the screen. V object = V + V 2
1
F = rV g
+ B 2 F = rVg
B
If P and Q are connected to the power supply, where V is the volume of the
2
cathode rays is deflected upwards and shadow of part of the body submerged in where V is the volume of the
body
the maltase cross is deflected upwards. the liquid
–
Important Facts (Chapter 5) 22 @ Pan Asia Publications Sdn. Bhd. Important Facts (Chapter 2) 16 @ Pan Asia Publications Sdn. Bhd.
4
• Equation for Alpha Decay (α or) He Internal Resistance
2
Parent nucleus has nucleon number, A and proton number, Z.
After a α-decay, the daughter nucleus has a nucleon number, The internal resistance of a dry cell is the obstruction or resistance
A – 4 and a proton number, Z – 2.
to the flow of charge by chemicals electrolyte in the dry cell.
4
A
X ˜ A–4 X + He + Energy
Z Z–2 2
0
• Equation for Beta Decay (β or) e
–1
Parent nucleus with nucleon number, A and proton number, Z.
After a β-decay, the daughter nucleus has a nucleon number, A
(no change) and a proton number, Z + 1. V Rheostat
0
A X ˜ A–0 X + e + Energy
Z Z+1 –1
• Equation for Gamma Decay (γ) A
There is no changes in nucleon number and proton number. The
nucleus is less energetic after gamma decay.
Ԑ = IR + Ir that is, V = IR
A
A X ˜ X + γ + Energy
Z Z Ԑ = V + Ir
Important Facts (Chapter 6) 24 @ Pan Asia Publications Sdn. Bhd. Important Facts (Chapter 3) 18 @ Pan Asia Publications Sdn. Bhd.
Must know_1202 Physic F5.indd 4 07/01/2022 11:41 AM