Page 397 - Math Smart - 7
P. 397
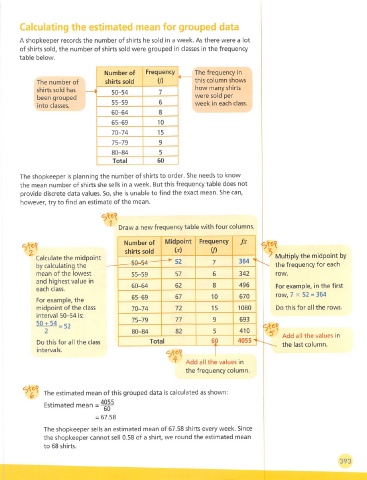
Calculating the estimated mean for grouped data
A shopkeeper records the number of shirts he sold In a week. As there were a lot
of shirts sold, the number of shirts sold were grouped in classes in the frequency
table below.
Number of Frequency The frequency in
The number of shirts sold (/) this column shows
how many shirts
shirts sold has
50-54 7
been grouped were sold per
55-59 6 week in each class.
into classes.
60-64 8
65-69 10
70-74 15
75-79 9
80-84 5
Total 60
The shopkeeper is planning the number of shirts to order. She needs to know
the mean number of shirts she sells in a week. But this frequency table does not
provide discrete data values. So, she is unable to find the exact mean. She can,
however, try to find an estimate of the mean.
1
Draw a new frequency table with four columns.
Midpoint Frequency
Number of fx
shirts sold (X) if) 5 Multiply the midpoint by
Calculate the midpoint
—^ 52 7 364 ^
by calculating the - the frequency for each
mean of the lowest 55-59 57 6 342 row.
and highest value in
60-64 62 8 496 For example, in the first
each class.
row, 7 X 52 = 364
65-69 67 10 670
For example, the
midpoint of the class 70-74 72 15 1080 Do this for all the rows.
interval 50-54 is:
75-79 77 9 693
50 + 54 _ ^2
80-84 82 5 410
Add all the values in
Do this for all the class Total 60 4055-
the last column.
intervals.
I
' Add all the values in
the frequency column.
The estimated mean of this grouped data is calculated as shown:
Estimated mean
= 67.58
The shopkeeper sells an estimated mean of 67.58 shirts every week. Since
the shopkeeper cannot sell 0.58 of a shirt, we round the estimated mean
to 68 shirts.
393