Page 32 - Basic Principles of Textile Coloration
P. 32
Moisture regain/ % PROPERTIES OF FIBRES 21
some surface lubricants and other chemicals added to facilitate processing. These
are relatively easy to remove compared to the difficulty of purifying natural fibres.
Water absorption is one of the key properties of a textile fibre. Protein or
cellulosic fibres are hydrophilic and absorb large amounts of water, which causes
radial swelling. Hydrophobic synthetic fibres, such as polyester, however, absorb
almost no water and do not swell. The hydrophilic or hydrophobic character of a
fibre influences the types of dyes that it will absorb. Dyeing in a wide range of hues
and depths is a key requirement for almost all textile materials.
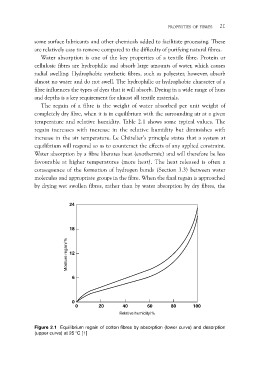
The regain of a fibre is the weight of water absorbed per unit weight of
completely dry fibre, when it is in equilibrium with the surrounding air at a given
temperature and relative humidity. Table 2.1 shows some typical values. The
regain increases with increase in the relative humidity but diminishes with
increase in the air temperature. Le Châtelier’s principle states that a system at
equilibrium will respond so as to counteract the effects of any applied constraint.
Water absorption by a fibre liberates heat (exothermic) and will therefore be less
favourable at higher temperatures (more heat). The heat released is often a
consequence of the formation of hydrogen bonds (Section 3.3) between water
molecules and appropriate groups in the fibre. When the final regain is approached
by drying wet swollen fibres, rather than by water absorption by dry fibres, the
24
18
12
6
0
0 20 40 60 80 100
Relative humidity/ %
Figure 2.1 Equilibrium regain of cotton fibres by absorption (lower curve) and desorption
(upper curve) at 25 °C [1]