Page 30 - Basic Principles of Textile Coloration
P. 30
REFERENCES 19
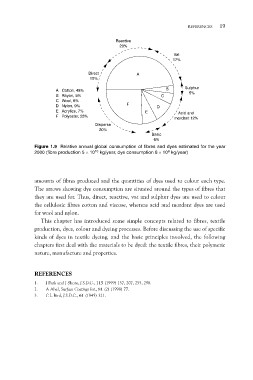
Reactive
20%
Vat
17%
Direct A
10%
A Cotton, 48% B Sulphur
B Rayon, 5% 5%
C Wool, 6%
D Nylon, 9% C
E Acrylics, 7%
F Polyester, 25% FD
E Acid and
mordant 12%
Disperse
20%
Basic
6%
Figure 1.9 Relative annual global consumption of fibres and dyes estimated for the year
2000 (fibre production 5 ´ 1010 kg/year, dye consumption 8 ´ 108 kg/year)
amounts of fibres produced and the quantities of dyes used to colour each type.
The arrows showing dye consumption are situated around the types of fibres that
they are used for. Thus, direct, reactive, vat and sulphur dyes are used to colour
the cellulosic fibres cotton and viscose, whereas acid and mordant dyes are used
for wool and nylon.
This chapter has introduced some simple concepts related to fibres, textile
production, dyes, colour and dyeing processes. Before discussing the use of specific
kinds of dyes in textile dyeing, and the basic principles involved, the following
chapters first deal with the materials to be dyed: the textile fibres, their polymeric
nature, manufacture and properties.
REFERENCES
1. J Park and J Shore, J.S.D.C., 115 (1999) 157, 207, 255, 298.
2. A Abel, Surface Coatings Int., 81 (2) (1998) 77.
3. C L Bird, J.S.D.C., 61 (1945) 321.