Page 413 - Basic Principles of Textile Coloration
P. 413
402 DYES SYNTHESISED IN THE FIBRE
solution of a dispersing agent, before addition to the aqueous alkali solution. Soft
water is essential to avoid precipitation of the insoluble calcium and magnesium
naphtholates. Many Naphtols are available as liquids that only require dilution and
additional alkali. Although the liquid forms are more expensive, their use does
avoid many of the problems associated with bath preparation.
Sometimes, the addition of formaldehyde to a concentrated Naphtol solution at
room temperature is recommended. This forms the 1-hydroxymethyl derivative
that prevents hydrolysis of naphtholate ion to the insoluble free phenol. The 1-
hydroxymethyl-2-naphthol is much more acidic than the original Naphtol because
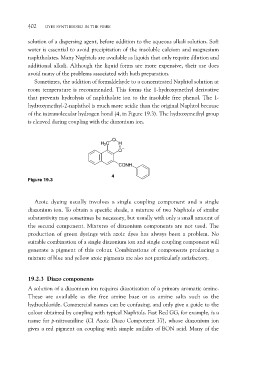
of the intramolecular hydrogen bond (4, in Figure 19.3). The hydroxymethyl group
is cleaved during coupling with the diazonium ion.
Figure 19.3 O
H2C H
O
CONH
4
Azoic dyeing usually involves a single coupling component and a single
diazonium ion. To obtain a specific shade, a mixture of two Naphtols of similar
substantivity may sometimes be necessary, but usually with only a small amount of
the second component. Mixtures of diazonium components are not used. The
production of green dyeings with azoic dyes has always been a problem. No
suitable combination of a single diazonium ion and single coupling component will
generate a pigment of this colour. Combinations of components producing a
mixture of blue and yellow azoic pigments are also not particularly satisfactory.
19.2.3 Diazo components
A solution of a diazonium ion requires diazotisation of a primary aromatic amine.
These are available as the free amine base or as amine salts such as the
hydrochloride. Commercial names can be confusing, and only give a guide to the
colour obtained by coupling with typical Naphtols. Fast Red GG, for example, is a
name for p-nitroaniline (CI Azoic Diazo Component 37), whose diazonium ion
gives a red pigment on coupling with simple anilides of BON acid. Many of the